Chapter 14. Inductance
14.4 RL Circuits
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Analyze circuits that have an inductor and resistor in series
- Describe how current and voltage exponentially grow or decay based on the initial conditions
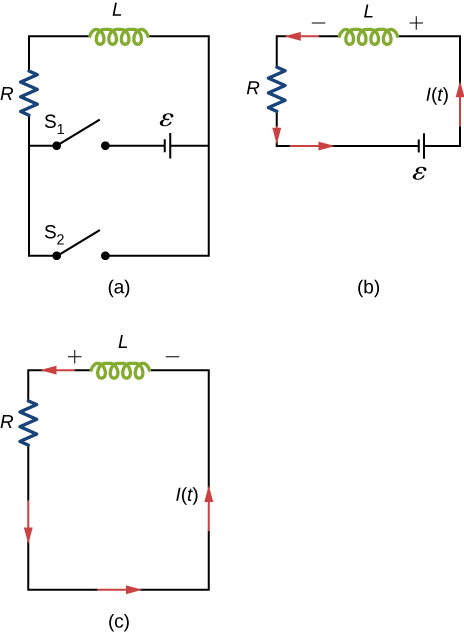
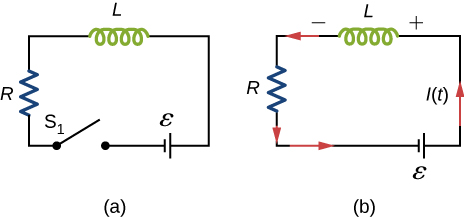
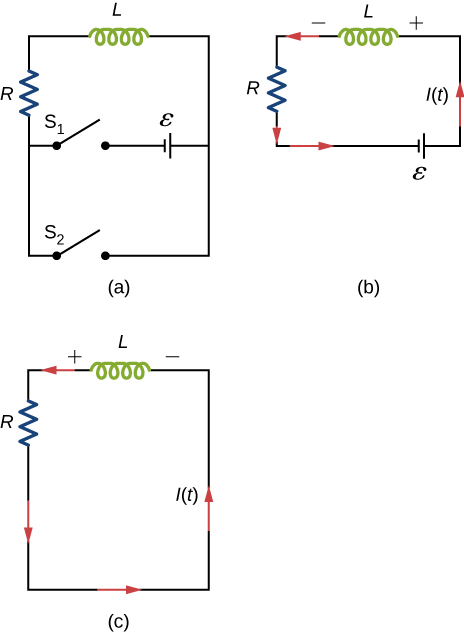
A circuit with resistance and self-inductance is known as an RL circuit. Figure 14.12(a) shows an RL circuit consisting of a resistor, an inductor, a constant source of emf, and switches [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}.[/latex] When [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is closed, the circuit is equivalent to a single-loop circuit consisting of a resistor and an inductor connected across a source of emf (Figure 14.12(b)). When [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is opened and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] is closed, the circuit becomes a single-loop circuit with only a resistor and an inductor (Figure 14.12(c)).
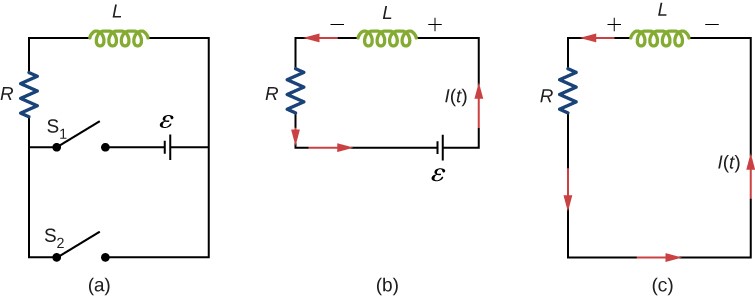
We first consider the RL circuit of Figure 14.12(b). Once [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is closed and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] is open, the source of emf produces a current in the circuit. If there were no self-inductance in the circuit, the current would rise immediately to a steady value of [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R.[/latex] However, from Faraday’s law, the increasing current produces an emf [latex]{V}_{L}=\text{−}L\left(dI\text{/}dt\right)[/latex] across the inductor. In accordance with Lenz’s law, the induced emf counteracts the increase in the current and is directed as shown in the figure. As a result, I(t) starts at zero and increases asymptotically to its final value.
Applying Kirchhoff’s loop rule to this circuit, we obtain
which is a first-order differential equation for I(t). Notice its similarity to the equation for a capacitor and resistor in series (See RC Circuits). Similarly, the solution to Equation 14.23 can be found by making substitutions in the equations relating the capacitor to the inductor. This gives
where
is the inductive time constant of the circuit.
The current I(t) is plotted in Figure 14.13(a). It starts at zero, and as [latex]t\to \infty[/latex], I(t) approaches [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R[/latex] asymptotically. The induced emf [latex]{V}_{L}\left(t\right)[/latex] is directly proportional to dI/dt, or the slope of the curve. Hence, while at its greatest immediately after the switches are thrown, the induced emf decreases to zero with time as the current approaches its final value of [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R.[/latex] The circuit then becomes equivalent to a resistor connected across a source of emf.
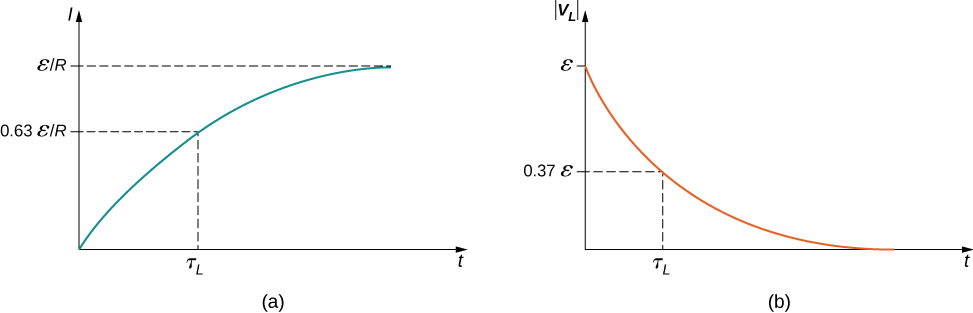
The energy stored in the magnetic field of an inductor is
Thus, as the current approaches the maximum current [latex]\epsilon \text{/}R[/latex], the stored energy in the inductor increases from zero and asymptotically approaches a maximum of [latex]L{\left(\epsilon \text{/}R\right)}^{2}\text{/}2.[/latex]
The time constant [latex]{\tau }_{L}[/latex] tells us how rapidly the current increases to its final value. At [latex]t={\tau }_{L},[/latex] the current in the circuit is, from Equation 14.24,
which is [latex]63\text{%}[/latex] of the final value [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R[/latex]. The smaller the inductive time constant [latex]{\tau }_{L}=L\text{/}R,[/latex] the more rapidly the current approaches [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R[/latex].
We can find the time dependence of the induced voltage across the inductor in this circuit by using [latex]{V}_{L}\left(t\right)=\text{−}L\left(dI\text{/}dt\right)[/latex] and Equation 14.24:
The magnitude of this function is plotted in Figure 14.13(b). The greatest value of [latex]L\left(dI\text{/}dt\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{is}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\epsilon ;[/latex] it occurs when dI/dt is greatest, which is immediately after [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is closed and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] is opened. In the approach to steady state, dI/dt decreases to zero. As a result, the voltage across the inductor also vanishes as [latex]t\to \infty .[/latex]
The time constant [latex]{\tau }_{L}[/latex] also tells us how quickly the induced voltage decays. At [latex]t={\tau }_{L},[/latex] the magnitude of the induced voltage is
The voltage across the inductor therefore drops to about [latex]37\text{%}[/latex] of its initial value after one time constant. The shorter the time constant [latex]{\tau }_{L},[/latex] the more rapidly the voltage decreases.
After enough time has elapsed so that the current has essentially reached its final value, the positions of the switches in Figure 14.12(a) are reversed, giving us the circuit in part (c). At [latex]t=0,[/latex] the current in the circuit is [latex]I\left(0\right)=\epsilon \text{/}R.[/latex] With Kirchhoff’s loop rule, we obtain
The solution to this equation is similar to the solution of the equation for a discharging capacitor, with similar substitutions. The current at time t is then
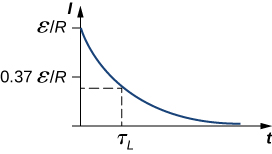
The current starts at [latex]I\left(0\right)=\epsilon \text{/}R[/latex] and decreases with time as the energy stored in the inductor is depleted (Figure 14.14).
The time dependence of the voltage across the inductor can be determined from [latex]{V}_{L}=\text{−}L\left(dI\text{/}dt\right)\text{:}[/latex]
This voltage is initially [latex]{V}_{L}\left(0\right)=\epsilon[/latex], and it decays to zero like the current. The energy stored in the magnetic field of the inductor, [latex]L{I}^{2}\text{/}2,[/latex] also decreases exponentially with time, as it is dissipated by Joule heating in the resistance of the circuit.
Example
An RL Circuit with a Source of emf
In the circuit of Figure 14.12(a), let [latex]\epsilon =2.0V,R=4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω},\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{and}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}L=4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{H}\text{.}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}[/latex] With [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] closed and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] open (Figure 14.12(b)), (a) what is the time constant of the circuit? (b) What are the current in the circuit and the magnitude of the induced emf across the inductor at [latex]t=0,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{at}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}t=2.0{\tau }_{L}[/latex], and as [latex]t\to \infty[/latex]?
Strategy
The time constant for an inductor and resistor in a series circuit is calculated using Equation 14.25. The current through and voltage across the inductor are calculated by the scenarios detailed from Figure 14.24 and Equation 14.32.
Solution
Show Answer
- The inductive time constant is
[latex]{\tau }_{L}=\frac{L}{R}=\frac{4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{H}}{4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω}}=1.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}.[/latex] - The current in the circuit of Figure 14.12(b) increases according to Equation 14.24:
[latex]I\left(t\right)=\frac{\text{ε}}{R}\left(1-{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}\right).[/latex]
At [latex]t=0,[/latex]
[latex]\left(1-{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}\right)=\left(1-1\right)=0;\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{so}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}I\left(0\right)=0.[/latex]
At [latex]t=2.0{\tau }_{L}[/latex] and [latex]t\to \infty ,[/latex] we have, respectively,
[latex]I\left(2.0{\tau }_{L}\right)=\frac{\text{ε}}{R}\left(1-{e}^{-2.0}\right)=\left(0.50\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{A}\right)\left(0.86\right)=0.43\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{A},[/latex]
and
[latex]I\left(\infty \right)=\frac{\text{ε}}{R}=0.50\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{A}.[/latex]
From Equation 14.32, the magnitude of the induced emf decays as
[latex]|{V}_{L}\left(t\right)|=\text{ε}{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}.[/latex]
[latex]\text{At}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}t=0,t=2.0{\tau }_{L},\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{and as}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}t\to \infty ,[/latex] we obtain
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill |{V}_{L}\left(0\right)|& =\hfill & \epsilon =2.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V},\hfill \\ \hfill |{V}_{L}\left(2.0{\tau }_{L}\right)|& =\hfill & \left(2.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{e}^{-2.0}=0.27\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}\hfill \\ & \text{and}\hfill & \\ \hfill |{V}_{L}\left(\infty \right)|& =\hfill & 0.\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Significance
If the time of the measurement were much larger than the time constant, we would not see the decay or growth of the voltage across the inductor or resistor. The circuit would quickly reach the asymptotic values for both of these. See Figure 14.15.
Example
An RL Circuit without a Source of emf
After the current in the RL circuit of Example 14.4 has reached its final value, the positions of the switches are reversed so that the circuit becomes the one shown in Figure 14.12(c). (a) How long does it take the current to drop to half its initial value? (b) How long does it take before the energy stored in the inductor is reduced to [latex]1.0\text{%}[/latex] of its maximum value?
Strategy
The current in the inductor will now decrease as the resistor dissipates this energy. Therefore, the current falls as an exponential decay. We can also use that same relationship as a substitution for the energy in an inductor formula to find how the energy decreases at different time intervals.
Solution
Show Answer
- With the switches reversed, the current decreases according to
[latex]I\left(t\right)=\frac{\epsilon }{R}{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}=I\left(0\right){e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}.[/latex]
At a time t when the current is one-half its initial value, we have
[latex]I\left(t\right)=0.50I\left(0\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{so}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}=0.50,[/latex]
and
[latex]t=\text{−}\left[\text{ln}\left(0.50\right)\right]{\tau }_{L}=0.69\left(1.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}\right)=0.69\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s},[/latex]
where we have used the inductive time constant found in Example 14.4. - The energy stored in the inductor is given by
[latex]{U}_{L}\left(t\right)=\frac{1}{2}L{\left[I\left(t\right)\right]}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}L{\left(\frac{\epsilon }{R}{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}\right)}^{2}=\frac{L{\epsilon }^{2}}{2{R}^{2}}{e}^{-2t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}.[/latex]
If the energy drops to [latex]1.0\text{%}[/latex] of its initial value at a time t, we have
[latex]{U}_{L}\left(t\right)=\left(0.010\right){U}_{L}\left(0\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{or}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{L{\epsilon }^{2}}{2{R}^{2}}{e}^{-2t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}=\left(0.010\right)\frac{L{\epsilon }^{2}}{2{R}^{2}}.[/latex]
Upon canceling terms and taking the natural logarithm of both sides, we obtain
[latex]-\frac{2t}{{\tau }_{L}}=\text{ln}\left(0.010\right),[/latex]
so
[latex]t=-\frac{1}{2}{\tau }_{L}\text{ln}\left(0.010\right).[/latex]
Since [latex]{\tau }_{L}=1.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}[/latex], the time it takes for the energy stored in the inductor to decrease to [latex]1.0\text{%}[/latex] of its initial value is
[latex]t=-\frac{1}{2}\left(1.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}\right)\text{ln}\left(0.010\right)=2.3\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}.[/latex]
Significance
This calculation only works if the circuit is at maximum current in situation (b) prior to this new situation. Otherwise, we start with a lower initial current, which will decay by the same relationship.
Check Your Understanding
Verify that RC and L/R have the dimensions of time.
Check Your Understanding
(a) If the current in the circuit of in Figure 14.12(b) increases to [latex]90\text{%}[/latex] of its final value after 5.0 s, what is the inductive time constant? (b) If [latex]R=20\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω}[/latex], what is the value of the self-inductance? (c) If the [latex]20\text{-}\text{Ω}[/latex] resistor is replaced with a [latex]100\text{-}\text{Ω}[/latex] resister, what is the time taken for the current to reach [latex]90\text{%}[/latex] of its final value?
Show Solution
a. 2.2 s; b. 43 H; c. 1.0 s
Check Your Understanding
For the circuit of in Figure 14.12(b), show that when steady state is reached, the difference in the total energies produced by the battery and dissipated in the resistor is equal to the energy stored in the magnetic field of the coil.
Summary
- When a series connection of a resistor and an inductor—an RL circuit—is connected to a voltage source, the time variation of the current is
[latex]I\left(t\right)=\frac{\text{ε}}{R}\left(1-{e}^{\text{−}Rt\text{/}L}\right)=\frac{\text{ε}}{R}\left(1-{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}\right)[/latex] (turning on),
where the initial current is [latex]{I}_{0}=\epsilon \text{/}R.[/latex] - The characteristic time constant [latex]\tau[/latex] is [latex]{\tau }_{L}=L\text{/}R,[/latex] where L is the inductance and R is the resistance.
- In the first time constant [latex]\tau ,[/latex] the current rises from zero to [latex]0.632{I}_{0},[/latex] and to 0.632 of the remainder in every subsequent time interval [latex]\tau .[/latex]
- When the inductor is shorted through a resistor, current decreases as
[latex]I\left(t\right)=\frac{\epsilon }{R}{e}^{\text{−}t\text{/}{\tau }_{L}}[/latex] (turning off).
Current falls to [latex]0.368{I}_{0}[/latex] in the first time interval [latex]\tau[/latex], and to 0.368 of the remainder toward zero in each subsequent time [latex]\tau .[/latex]
Conceptual Questions
Use Lenz’s law to explain why the initial current in the RL circuit of Figure 14.12(b) is zero.
Show Solution
As current flows through the inductor, there is a back current by Lenz’s law that is created to keep the net current at zero amps, the initial current.
When the current in the RL circuit of Figure 14.12(b) reaches its final value [latex]\text{ε}\text{/}R,[/latex] what is the voltage across the inductor? Across the resistor?
Does the time required for the current in an RL circuit to reach any fraction of its steady-state value depend on the emf of the battery?
Show Solution
no
An inductor is connected across the terminals of a battery. Does the current that eventually flows through the inductor depend on the internal resistance of the battery? Does the time required for the current to reach its final value depend on this resistance?
At what time is the voltage across the inductor of the RL circuit of Figure 14.12(b) a maximum?
Show Solution
At [latex]t=0[/latex], or when the switch is first thrown.
In the simple RL circuit of Figure 14.12(b), can the emf induced across the inductor ever be greater than the emf of the battery used to produce the current?
If the emf of the battery of Figure 14.12(b) is reduced by a factor of 2, by how much does the steady-state energy stored in the magnetic field of the inductor change?
Show Solution
1/4
A steady current flows through a circuit with a large inductive time constant. When a switch in the circuit is opened, a large spark occurs across the terminals of the switch. Explain.
Describe how the currents through [latex]{R}_{1}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{and}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{R}_{2}[/latex] shown below vary with time after switch S is closed.
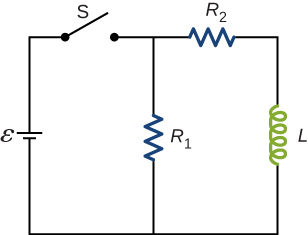
Show Solution
Initially, [latex]{I}_{R1}=\frac{\epsilon }{{R}_{1}}[/latex] and [latex]{I}_{R2}=0[/latex], and after a long time has passed, [latex]{I}_{R1}=\frac{\epsilon }{{R}_{1}}[/latex] and [latex]{I}_{R2}=\frac{\epsilon }{{R}_{2}}[/latex].
Discuss possible practical applications of RL circuits.
Problems
In Figure 14.12, [latex]\epsilon =12\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}[/latex], [latex]L=20\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{mH}[/latex], and [latex]R=5.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω}[/latex]. Determine (a) the time constant of the circuit, (b) the initial current through the resistor, (c) the final current through the resistor, (d) the current through the resistor when [latex]t=2{\tau }_{L},[/latex] and (e) the voltages across the inductor and the resistor when [latex]t=2{\tau }_{L}.[/latex]
For the circuit shown below, [latex]\epsilon =20\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}[/latex], [latex]L=4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{mH,}[/latex] and [latex]R=5.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω}[/latex]. After steady state is reached with [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] closed and [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] open, [latex]{\text{S}}_{2}[/latex] is closed and immediately thereafter [latex]\left(\text{at}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}t=0\right)[/latex] [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is opened. Determine (a) the current through L at [latex]t=0[/latex], (b) the current through L at [latex]t=4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{10}^{-4}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}[/latex], and (c) the voltages across L and R at [latex]t=4.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{10}^{-4}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}[/latex].
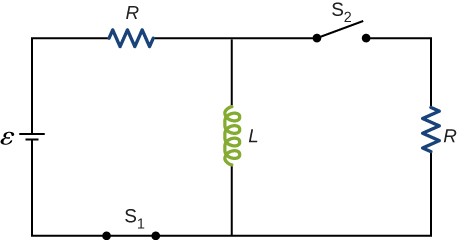
Show Solution
a. 4.0 A; b. 2.4 A; c. on R: [latex]V=12\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}[/latex]; on L: [latex]V=7.9\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}[/latex]
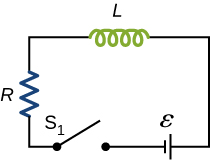
The current in the RL circuit shown here increases to [latex]40\text{%}[/latex] of its steady-state value in 2.0 s. What is the time constant of the circuit?
How long after switch [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is thrown does it take the current in the circuit shown to reach half its maximum value? Express your answer in terms of the time constant of the circuit.
Show Solution
[latex]0.69\tau[/latex]
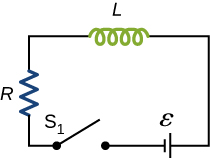
Examine the circuit shown below in part (a). Determine dI/dt at the instant after the switch is thrown in the circuit of (a), thereby producing the circuit of (b). Show that if I were to continue to increase at this initial rate, it would reach its maximum [latex]\epsilon \text{/}R[/latex] in one time constant.
The current in the RL circuit shown below reaches half its maximum value in 1.75 ms after the switch [latex]{\text{S}}_{1}[/latex] is thrown. Determine (a) the time constant of the circuit and (b) the resistance of the circuit if [latex]L=250\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{mH}[/latex].
Show Solution
a. 2.52 ms; b. [latex]99.2\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω}[/latex]
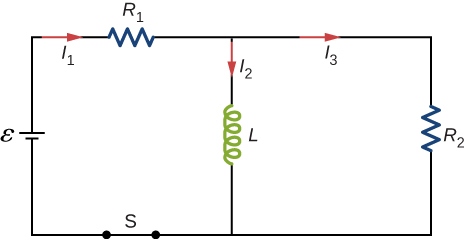
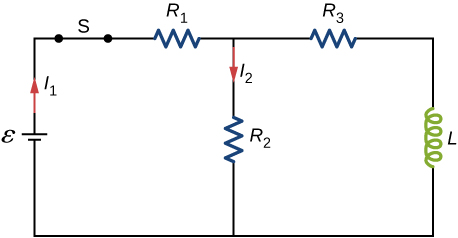
Consider the circuit shown below. Find [latex]{I}_{1},{I}_{2},\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{and}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{I}_{3}[/latex] when (a) the switch S is first closed, (b) after the currents have reached steady-state values, and (c) at the instant the switch is reopened (after being closed for a long time).
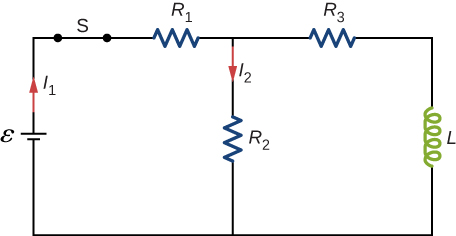
For the circuit shown below, [latex]\epsilon =50\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{V}[/latex], [latex]{R}_{1}=10\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ω,}[/latex], [latex]{R}_{2}={R}_{3}=\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{19.4 Ω,}[/latex], and [latex]L=2.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{mH}[/latex]. Find the values of [latex]{I}_{1}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{and}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{I}_{2}[/latex] (a) immediately after switch S is closed, (b) a long time after S is closed, (c) immediately after S is reopened, and (d) a long time after S is reopened.
Show Solution
a. [latex]{I}_{1}={I}_{2}=1.7\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}A[/latex]; b. [latex]{I}_{1}=2.73\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}A,{I}_{2}=1.36\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}A[/latex]; c. [latex]{I}_{1}=0,{I}_{2}=0.54\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}A[/latex]; d. [latex]{I}_{1}={I}_{2}=0[/latex]
For the circuit shown below, find the current through the inductor [latex]2.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{10}^{-5}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{s}[/latex] after the switch is reopened.
Show that for the circuit shown below, the initial energy stored in the inductor, [latex]L{I}^{2}\left(0\right)\text{/}2[/latex], is equal to the total energy eventually dissipated in the resistor, [latex]{\int }_{0}^{\infty }{I}^{2}\left(t\right)Rdt[/latex].
Show Solution
proof
Glossary
- inductive time constant
- denoted by [latex]\tau[/latex], the characteristic time given by quantity L/R of a particular series RL circuit
Licenses and Attributions
RL Circuits. Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-2/pages/14-4-rl-circuits. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-2/pages/1-introduction

