Introduction to Viruses
Introduction
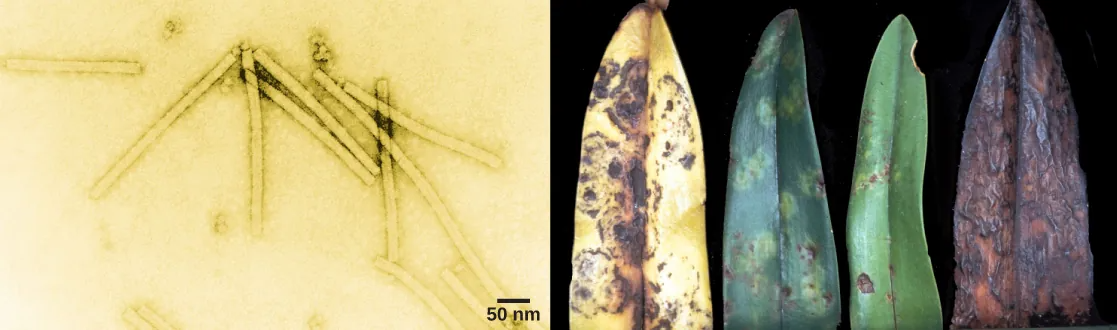
Viruses are noncellular parasitic entities that cannot be classified within any kingdom. They can infect organisms as diverse as bacteria, plants, and animals. In fact, viruses exist in a sort of netherworld between a living organism and a nonliving entity. Living things grow, metabolize, and reproduce. In contrast, viruses are not cellular, do not have a metabolism or grow, and cannot divide by cell division. Viruses can copy, or replicate themselves; however, they are entirely dependent on resources derived from their host cells to produce progeny viruses—which are assembled in their mature form. No one knows exactly when or how viruses evolved or from what ancestral source because viruses have not left a fossil record. Some virologists contend that modern viruses are a mosaic of bits and pieces of nucleic acids picked up from various sources along their respective evolutionary paths.

