26.3 Angiosperms
Learning Outcomes
- Explain why angiosperms are the dominant form of plant life in most terrestrial ecosystems
- Describe the main parts of a flower and their functions
- Detail the life cycle of a typical gymnosperm and angiosperm
- Discuss the similarities and differences between the two main groups of flowering plants
From their humble and still obscure beginning during the early Jurassic period, the angiosperms (flowering plants) have evolved to dominate most terrestrial ecosystems (Figure 26.13). With more than 300,000 species, the angiosperm phylum (Anthophyta) is second only to insects in terms of diversification.

The success of angiosperms is due to two novel reproductive structures: flowers and fruits. The function of the flower is to ensure pollination, often insects, as well as to protect the developing embryo. The colors and patterns on flowers offer specific signals to many pollinating insects, birds, and bats that have coevolved with them. For example, some patterns are visible only in the ultraviolet range of light, which can be seen by insect pollinators. For some pollinators, flowers advertise themselves as a reliable source of nectar. Flower scent also helps to select its pollinators. Flowers also provide protection for the ovule and developing embryo inside a receptacle. The function of the fruit is seed protection and dispersal. Different fruit structures or tissues on fruit—such as sweet flesh, wings, parachutes, or spines that grab—reflect the dispersal strategies that help spread seeds.
Flowers
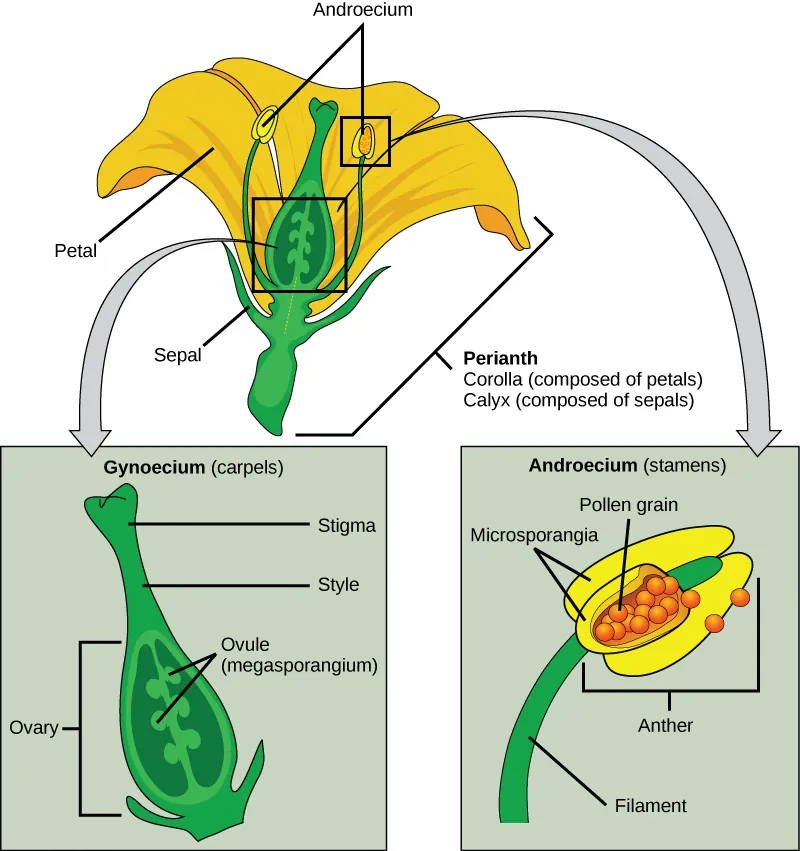
Flowers are modified leaves organized around a central receptacle. Although they vary greatly in appearance, virtually all flowers contain the same structures: sepals, petals, carpels, and stamens. The peduncle typically attaches the flower to the plant proper. A whorl of sepals (collectively called the calyx) is located at the base of the peduncle and encloses the unopened floral bud. Sepals are usually photosynthetic organs, although there are some exceptions. Petals, (collectively called the corolla) are located inside the whorl of sepals and may display vivid colors to attract pollinators. The sexual organs, the female gynoecium and male androecium are located at the center of the flower.
As illustrated in Figure 26.14, the innermost part of a perfect flower is the gynoecium, the location in the flower where the eggs will form. The female reproductive unit consists of one or more carpels, each of which has a stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is the location where the pollen is deposited either by wind or a pollinating arthropod. The sticky surface of the stigma traps pollen grains, and the style is a connecting structure through which the pollen tube will grow to reach the ovary. The ovary houses one or more ovules, each of which will ultimately develop into a seed. The androecium, the male reproductive region, is composed of multiple stamens surrounding the central carpel. Stamens are composed of a thin stalk called a filament and a sac-like structure called the anther. The filament supports the anther, where the microspores are produced by meiosis and develop into haploid pollen grains, or male gametophytes.
The Life Cycle of an Angiosperm
The adult or sporophyte phase is the main phase of an angiosperm’s life cycle (Figure 26.15). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are heterosporous. Therefore, they produce microspores, which will generate pollen grains as the male gametophytes, and megaspores, which will form an ovule that contains female gametophytes. Inside the anther’s microsporangia, male sporocytes divide by meiosis to generate haploid microspores, which, in turn, undergo mitosis and give rise to pollen grains. Each pollen grain contains two cells: one generative cell that will divide into two sperm and a second cell that will become the pollen tube cell.
Visual Connection
Life Cycle of an Angiosperm
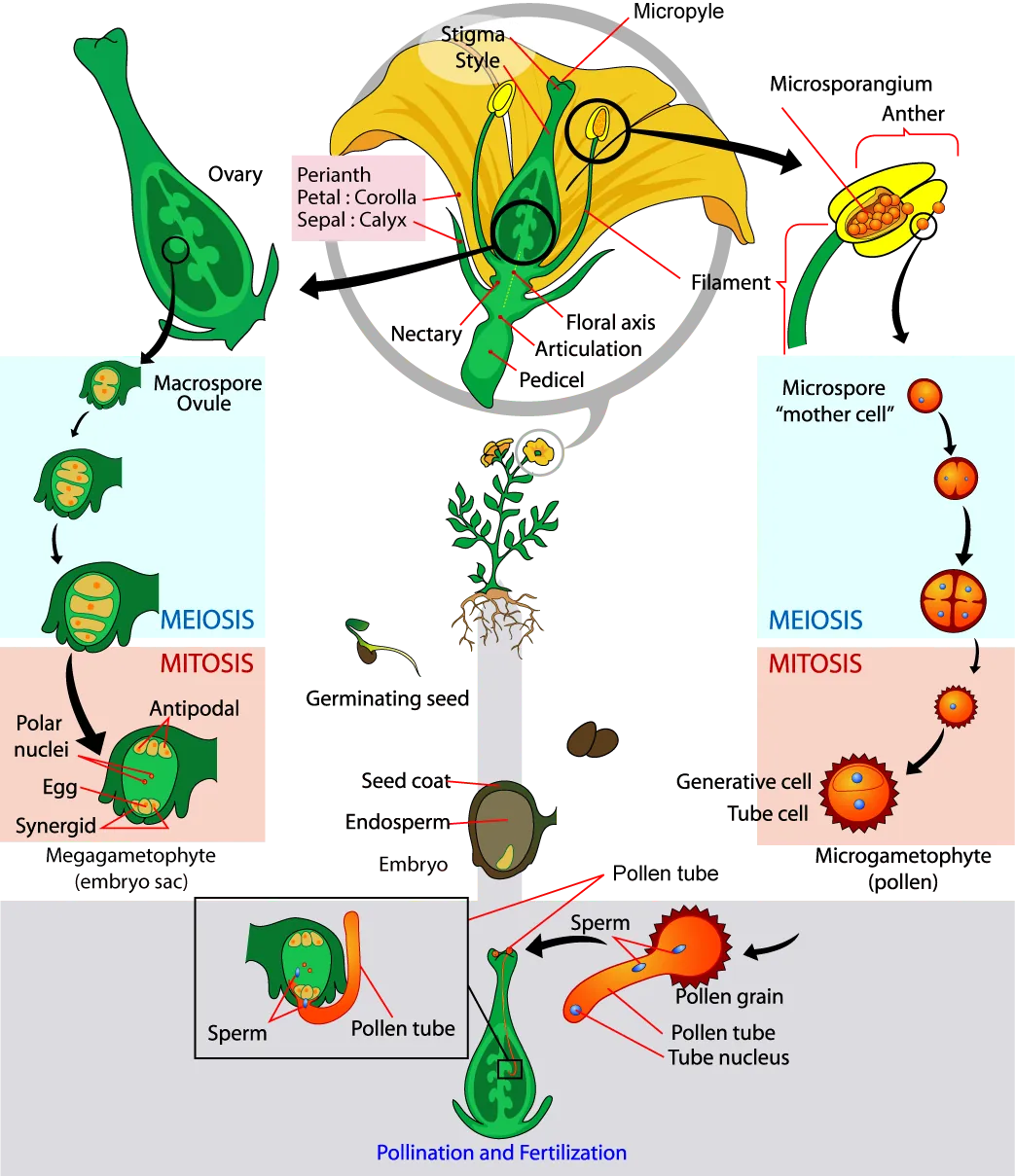
The ovule, sheltered within the ovary of the carpel, contains the megasporangium protected by two layers of integuments and the ovary wall. Within each megasporangium, a diploid megasporocyte undergoes meiosis, generating four haploid megaspores—three small and one large. Only the large megaspore survives; it divides mitotically three times to produce eight nuclei distributed among the seven cells of the female gametophyte or embryo sac. Three of these cells are located at each pole of the embryo sac. The three cells at one pole become the egg and two synergids. The three cells at the opposite pole become antipodal cells. The center cell contains the remaining two nuclei (polar nuclei). This cell will eventually produce the endosperm of the seed. The mature embryo sac then contains one egg cell, two synergids or “helper” cells, three antipodal cells (which eventually degenerate), and a central cell with two polar nuclei. When a pollen grain reaches the stigma, a pollen tube extends from the grain, grows down the style, and enters through the micropyle: an opening in the integuments of the ovule. The two sperm are deposited in the embryo sac.
A double fertilization event then occurs. One sperm and the egg combine, forming a diploid zygote—the future embryo. The other sperm fuses with the polar nuclei, forming a triploid cell that will develop into the endosperm—the tissue that serves as a food reserve for the developing embryo. The zygote develops into an embryo with a radicle, or small root, and one (monocot) or two (dicot) leaf-like organs called cotyledons. This difference in the number of embryonic leaves is the basis for the two major groups of angiosperms: the monocots and the eudicots. Seed food reserves are stored outside the embryo, in the form of complex carbohydrates, lipids, or proteins. The cotyledons serve as conduits to transmit the broken-down food reserves from their storage site inside the seed to the developing embryo. The seed consists of a toughened layer of integuments forming the coat, the endosperm with food reserves, and at the center, the well-protected embryo.
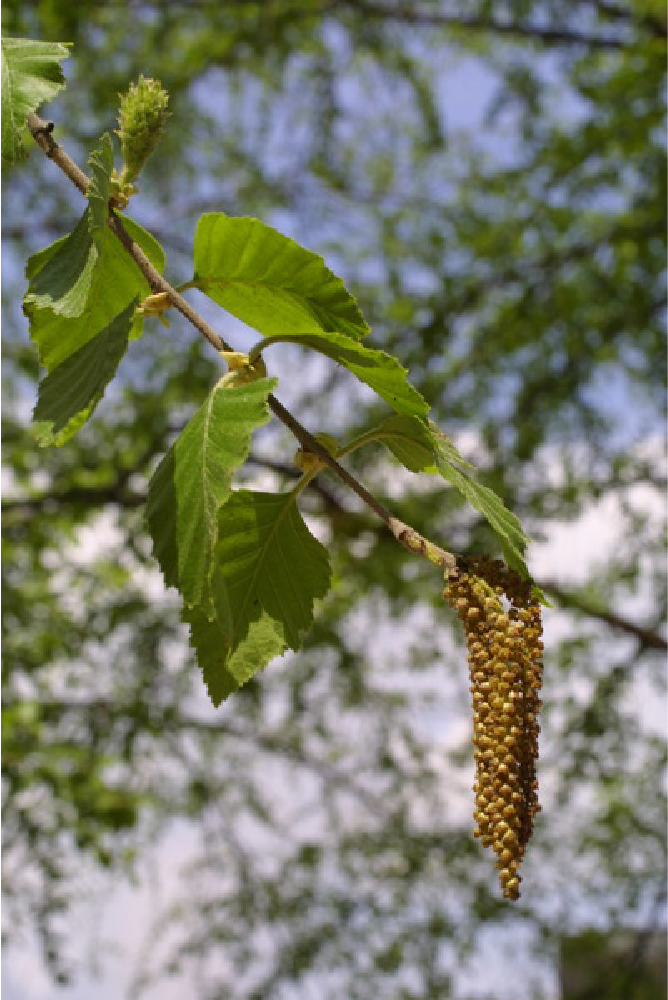

Most angiosperms have perfect flowers, which means that each flower carries both stamens and carpels (Figure 26.15). In monoecious plants, male (staminate) and female (pistillate) flowers are separate, but carried on the same plant. In dioecious plants, male and female flowers are found on separate plants. In spite of the predominance of perfect flowers, only a few species of angiosperms self-pollinate. Both anatomical and environmental barriers promote cross-pollination mediated by a physical agent (wind or water), or an animal, such as an insect or bird. Cross-pollination increases genetic diversity in a species.
The ovule, sheltered within the ovary of the carpel, contains the megasporangium protected by two layers of integuments and the ovary wall. Within each megasporangium, a diploid megasporocyte undergoes meiosis, generating four haploid megaspores—three small and one large. Only the large megaspore survives; it divides mitotically three times to produce eight nuclei distributed among the seven cells of the female gametophyte or embryo sac. Three of these cells are located at each pole of the embryo sac. The three cells at one pole become the egg and two synergids. The three cells at the opposite pole become antipodal cells. The center cell contains the remaining two nuclei (polar nuclei). This cell will eventually produce the endosperm of the seed. The mature embryo sac then contains one egg cell, two synergids or “helper” cells, three antipodal cells (which eventually degenerate), and a central cell with two polar nuclei. When a pollen grain reaches the stigma, a pollen tube extends from the grain, grows down the style, and enters through the micropyle: an opening in the integuments of the ovule. The two sperm are deposited in the embryo sac.
A double fertilization event then occurs. One sperm and the egg combine, forming a diploid zygote—the future embryo. The other sperm fuses with the polar nuclei, forming a triploid cell that will develop into the endosperm—the tissue that serves as a food reserve for the developing embryo. The zygote develops into an embryo with a radicle, or small root, and one (monocot) or two (dicot) leaf-like organs called cotyledons. This difference in the number of embryonic leaves is the basis for the two major groups of angiosperms: the monocots and the eudicots. Seed food reserves are stored outside the embryo, in the form of complex carbohydrates, lipids, or proteins. The cotyledons serve as conduits to transmit the broken-down food reserves from their storage site inside the seed to the developing embryo. The seed consists of a toughened layer of integuments forming the coat, the endosperm with food reserves, and at the center, the well-protected embryo.
Most angiosperms have perfect flowers, which means that each flower carries both stamens and carpels (Figure 26.15). In monoecious plants, male (staminate) and female (pistillate) flowers are separate, but carried on the same plant. In dioecious plants, male and female flowers are found on separate plants. In spite of the predominance of perfect flowers, only a few species of angiosperms self-pollinate. Both anatomical and environmental barriers promote cross-pollination mediated by a physical agent (wind or water), or an animal, such as an insect or bird. Cross-pollination increases genetic diversity in a species.
Fruit
As the seed develops, the walls of the ovary thicken and form the fruit. The seed forms in an ovary, which also enlarges as the seeds grow. Many foods commonly called vegetables are actually fruits. Eggplants, zucchini, tomatoes, and bell peppers are all technically fruits because they contain seeds and are derived from the thick ovary tissue. Botanists classify fruit into more than two dozen different categories, only a few of which are actually fleshy and sweet.
Mature fruit can be fleshy or dry. Fleshy fruit include the familiar berries, peaches, apples, grapes, and tomatoes. Rice, wheat, and nuts are examples of dry fruit. Another subtle distinction is that not all fruits are derived from just the ovary. For instance, strawberries are derived from the ovary as well as the receptacle, and apples are formed from the ovary and the pericarp. Some fruits are derived from separate ovaries in a single flower, such as the raspberry. Other fruits, such as the pineapple, form from clusters of flowers. Regardless of how they are formed, fruits are an agent of seed dispersal. The variety of shapes and characteristics reflect the mode of dispersal. Wind carries the light dry fruits of trees and dandelions. Water transports floating coconuts. Some fruits attract herbivores as food. Once eaten, tough, undigested seeds are dispersed through the herbivore’s feces. Other fruits have burrs and hooks to cling to fur and hitch rides on animals.
Diversity of Angiosperms
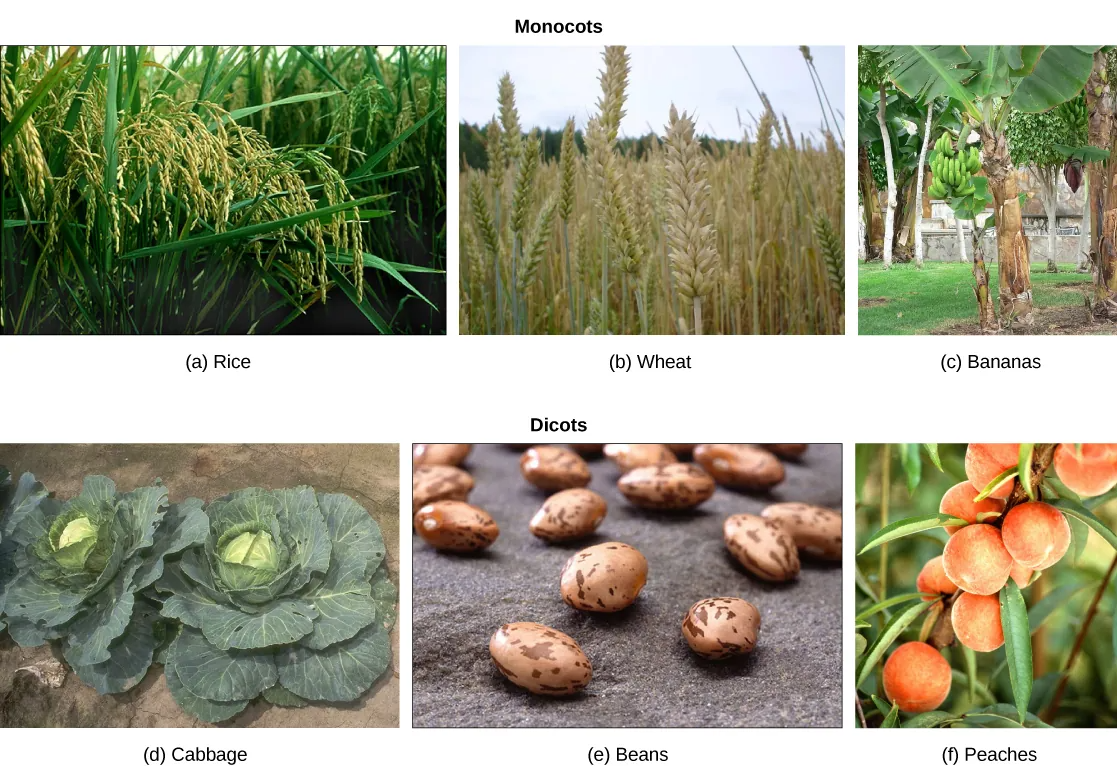
Angiosperms are classified in a single phylum: the Anthophyta. Modern angiosperms appear to be a monophyletic group, which as you may recall means that they originated from a single ancestor. Within the angiosperms are three major groups: basal angiosperms, monocots, and eudicots. Basal angiosperms are a group of plants that are believed to have branched off before the separation of the monocots and eudicots, because they exhibit traits from both groups. The monocots and eudicots are differentiated on the basis of the structure of the cotyledons, pollen grains, and other structures. Monocots include grasses and lilies, and the dicots form a multi-branched group that includes (among many others) roses, cabbages, sunflowers, and mints.
Monocots
Plants in the monocot group are primarily identified by the presence of a single cotyledon in the seedling. Other anatomical features shared by monocots include veins that run parallel to and along the length of the leaves, and flower parts that are arranged in a three- or six-fold symmetry. True woody tissue is rarely found in monocots. In palm trees, vascular and parenchyma tissues produced by the primary and secondary thickening meristems form the trunk. Vascular tissue of the stem is scattered, not arranged in any particular pattern, but is organized in a ring in the roots. The root system consists of multiple fibrous roots, with no major tap root. Adventitious roots often emerge from the stem or leaves. The monocots include familiar plants such as grasses, orchids, and palms. Many important crops are monocots, such as rice and other cereals, corn, sugar cane, and tropical fruits like bananas and pineapples (Figure 26.19a,b,c).

Eudicots
Eudicots, or true dicots, are characterized by the presence of two cotyledons in the developing shoot. Veins form a network in leaves, and flower parts come in four, five, or many whorls. Vascular tissue forms a ring in the stem. Eudicots can be herbaceous (not woody), or woody. The root system is usually anchored by one main tap root. Eudicots comprise two-thirds of all flowering plants. The major differences between monocots and eudicots are summarized in Table 26.1.
| Comparison of Structural Characteristics of Monocots and Eudicots | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Monocot | Eudicot |
| Cotyledon | One | Two |
| Veins in Leaves | Parallel | Network (branched) |
| Stem Vascular Tissue | Scattered | Arranged in ring pattern |
| Roots | Network of fibrous roots | Tap root with many lateral roots |
| Flower Parts | Three or multiple of three | Four, five, multiple of four or five and whorls |

