Chapter 1: American Government and Civic Engagement
Who Governs? Elitism, Pluralism, and Tradeoffs
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the pluralism-elitism debate
- Explain the tradeoffs perspective on government
The United States allows its citizens to participate in government in many ways. The United States also has many different levels and branches of government that any citizen or group might approach. Many people take this as evidence that U.S. citizens, especially as represented by competing groups, are able to influence government actions. Some political theorists, however, argue that this is not the case. They claim that only a handful of economic and political elites have any influence over government.
ELITISM VS. PLURALISM
Many Americans fear that a set of elite citizens is really in charge of government in the United States and that others have no influence. This belief is called the elite theory of government. In contrast to that perspective is the pluralist theory of government, which says that political power rests with competing interest groups who share influence in government. Pluralist theorists assume that citizens who want to get involved in the system do so because of the great number of access points to government. That is, the U.S. system, with several levels and branches, has many places where people and groups can engage the government.
The foremost supporter of elite theory was C. Wright Mills. In his book, The Power Elite, Mills argued that government was controlled by a combination of business, military, and political elites.[1] Most are highly educated, often graduating from prestigious universities (Figure 1.6). According to elite theory, the wealthy use their power to control the nation’s economy in such a way that those below them cannot advance economically. Their wealth allows the elite to secure for themselves important positions in politics. They then use this power to make decisions and allocate resources in ways that benefit them. Politicians do the bidding of the wealthy instead of attending to the needs of ordinary people, and order is maintained by force. Indeed, those who favor government by the elite believe the elite are better fit to govern and that average citizens are content to allow them to do so.[2]
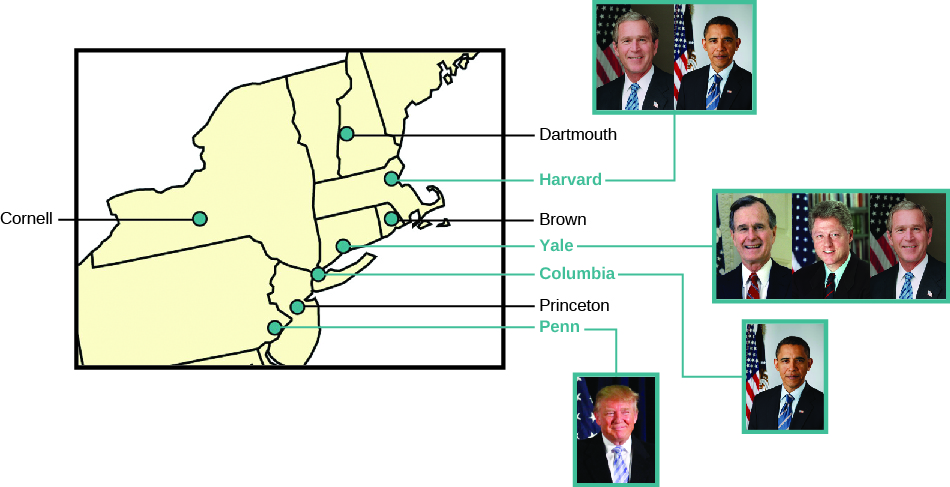
In apparent support of the elite perspective, one-third of U.S. presidents have attended Ivy League schools, a much higher percentage than the rest of the U.S. population.[3] Among members of the House of Representatives, 95 percent have a bachelor’s degree, as do 100 percent of members of the Senate.[4] Fewer than 40 percent of U.S. adults have even an associate’s degree.[5] The majority of the men and women in Congress also engaged in either state or local politics, were business people, or practiced law before being elected to Congress.[6] Approximately 73 percent of members of Congress are men, and about 76 percent are White.[7] The nation’s laws are made primarily by well-educated White male professionals and businessmen.
The makeup of Congress is important because race, gender, profession, education, and socioeconomic status have an important effect on people’s political interests. For example, changes in the way taxes are levied and spent do not affect all citizens equally. A flat tax, which generally requires that everyone pay the same percentage rate, hurts the poor more than it does the rich. If the income tax rate was flat at 10 percent, all Americans would have to pay 10 percent of their income to the federal government. Someone who made $40,000 a year would have to pay $4,000 and be left with only $36,000 to live on. Someone who made $1,000,000 would have to pay $100,000, a greater sum, but they would still be left with $900,000. People who were not wealthy would probably pay more than they could comfortably afford, while the wealthy, who could afford to pay more and still live well, would not see a real impact on their daily lives. Similarly, the allocation of revenue affects the rich and the poor differently. Giving more money to public education does not benefit the wealthy as much as it does the poor, because the wealthy are more likely than the poor to send their children to private schools or to at least have the option of doing so. However, better funded public schools have the potential to greatly improve the upward mobility of members of other socioeconomic classes who have no other option than to send their children to public schools.
Currently, about half of the members of Congress are millionaires.[8] As of 2009, approximately 38 percent of Congress sent their children to private schools. Overall, only 11 percent of the American population did so.[9] Therefore, a Congress dominated by millionaires who send their children to private schools is more likely to believe that a flat tax is fair and that increased funding for public education is not a necessity. Their experience, however, does not reflect the experience of average Americans.
Pluralist theory rejects this approach, arguing that although there are elite members of society they do not control government. Instead, pluralists argue, political power is distributed throughout society. Rather than resting in the hands of individuals, a variety of organized groups hold power, with some groups having more influence on certain issues than others. Thousands of interest groups exist in the United States.[10] Approximately 70–90 percent of Americans report belonging to at least one group.[11]
According to pluralist theory, people with shared interests will form groups in order to make their desires known to politicians. These groups include such entities as environmental advocates, unions, and organizations that represent the interests of various businesses. Because most people lack the inclination, time, or expertise necessary to decide political issues, these groups will speak for them. As groups compete with one another and find themselves in conflict regarding important issues, government policy begins to take shape. In this way, government policy is shaped from the bottom up and not from the top down, as we see in elitist theory. Robert Dahl, author of Who Governs?, was one of the first to advance the pluralist theory, and argued that politicians seeking an “electoral payoff” are attentive to the concerns of politically active citizens and, through them, become acquainted with the needs of ordinary people. They will attempt to give people what they want in exchange for their votes.[12]
LINK TO LEARNING
THE TRADEOFFS PERSPECTIVE
Although elitists and pluralists present political influence as a tug-of-war with people at opposite ends of a rope trying to gain control of government, in reality government action and public policy are influenced by an ongoing series of tradeoffs or compromises. For instance, an action that will meet the needs of large numbers of people may not be favored by the elite members of society. Giving the elite what they want may interfere with plans to help the poor. As pluralists argue, public policy is created as a result of competition among groups. In the end, the interests of both the elite and the people likely influence government action, and compromises will often attempt to please them both.
Since the framing of the U.S. Constitution, tradeoffs have been made between those who favor the supremacy of the central government and those who believe that state governments should be more powerful. With the rapid spread of COVID-19 in 2020, should the national government have been able able to mandate state and local actions on masks and social distancing in order to protect the public? Or, was the approach that played out, with state and local control of these measures, the way to go? Should those who control the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the National Security Agency (NSA) be allowed to eavesdrop on phone conversations of Americans and read their email? Should groups like the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU), which protect all citizens’ rights to freedom of speech, be able to prevent this?
Many of the tradeoffs made by government are about freedom of speech. The First Amendment of the Constitution gives Americans the right to express their opinions on matters of concern to them; the federal government cannot interfere with this right. Because of the Fourteenth Amendment, state governments must protect this right also. At the same time, neither the federal government nor state governments can allow someone’s right to free expression to interfere with someone else’s ability to exercise their own rights. For example, in the United States, it is legal for women to have abortions. Many people oppose this right and often protest outside facilities that provide abortions. In 2007, the state of Massachusetts enacted a law that required protestors to stand thirty-five feet away from clinic entrances. The intention was to prevent women seeking abortions from being harassed or threatened with violence. Groups favoring the protection of women’s reproductive rights supported the law. Groups opposed to abortion argued that the buffer zone prevented them from speaking to women to try to persuade them not to have the procedure done. In 2014, in the case of McCullen v. Coakley, the U.S. Supreme Court struck down the law that created a buffer zone between protestors and clinic entrances.[13] The federal government does not always side with those who oppose abortion, however. Several states have attempted to pass laws requiring women to notify their husbands, and often obtain their consent, before having an abortion. All such laws have been found unconstitutional by the courts.
Tradeoffs also occur as a result of conflict between groups representing the competing interests of citizens. Many Americans believe that the U.S. must become less dependent on foreign sources of energy. Many also would like people to have access to inexpensive sources of energy. Such people are likely to support fracking: the process of hydraulic fracturing that gives drilling companies access to natural gas trapped between layers of shale underground. Fracking produces abundant, inexpensive natural gas, a great benefit to people who live in parts of the country where it is expensive to heat homes during the winter. Fracking also creates jobs. At the same time, many scholars argue that fracking can result in the contamination of drinking water, air pollution, and increased risk of earthquakes. One study has even linked fracking to cancer. Thus, those who want to provide jobs and inexpensive natural gas are in conflict with those who wish to protect the natural environment and human health (Figure 1.7). Both sides are well intentioned, but they disagree over what is best for people.[14]

Tradeoffs are especially common in the United States Congress. Members of the Senate and the House of Representatives usually vote according to the concerns of people who live in their districts. Not only does this often pit the interests of people in different parts of the country against one another, but it also frequently favors the interests of certain groups of people over the interests of others within the same state. For example, allowing oil companies to drill off the state’s coast may please those who need the jobs that will be created, but it will anger those who wish to preserve coastal lands as a refuge for wildlife and, in the event of an accident, may harm the interests of people who depend on fishing and tourism for their living. At times, House members and senators in Congress may ignore the voters in their home states and the groups that represent them in order to follow the dictates of the leaders of the political party to which they belong. For example, a member of Congress from a state with a large elderly population may be inclined to vote in favor of legislation to increase benefits for retired people; however, the political party leaders, who disapprove of government spending on social programs, may ask for a vote against it. The opposite can occur as well, especially in the case of a legislator soon facing re-election. With two-year terms of office, we are more likely to see House members buck their party in favor of their constituents.
Finally, the government may attempt to resolve conflicting concerns within the nation as a whole through tradeoffs. After repeated incidents of mass shootings at schools, theaters, churches, concerts, night clubs, and shopping malls, many are concerned with protecting themselves and their families from firearm violence. Some groups would like to ban the sale of certain types of weapons completely. Some do not want to ban gun ownership; they merely want greater restrictions to be put in place on who can buy guns or how long people must wait between the time they enter the store to make a purchase and the time when they are actually given possession of the weapon. Others oppose any restrictions on the number or type of weapons Americans may own. So far, state governments have attempted to balance the interests of these groups by placing restrictions on such things as who can sell guns, where gun sales may take place, or requirements for background checks, but they have not attempted to ban gun sales altogether. For example, although federal law does not require private gun dealers (people who sell guns but do not derive most of their income from doing so) to conduct background checks before selling firearms to people at gun shows, some states have passed laws requiring this.[15]
At the federal level, there has been widespread support in Congress to improve the background checking process. Indeed, despite objections from the National Rifle Association, the Fix-NICS Act passed the House and Senate and was signed into law by President Trump as part of an omnibus spending bill in March 2018.[16] And, in the wake of mass shootings in Atlanta and Boulder, at the time of this writing, there are two House-passed bills under consideration in the U.S. Senate.[17]
CHAPTER REVIEW
See the Chapter 1.2 Review for a summary of this section, the key vocabulary, and some review questions to check your knowledge.
- C. Wright Mills. 1956. The Power Elite. New York: Oxford University Press. ↵
- Jack L. Walker. 1966. “A Critique of the Elitist Theory of Democracy,” The American Political Science Review 60, No. 2: 295. ↵
- The Ivy League is technically an athletic conference in the Northeast comprised of sports teams from eight institutions of higher education—Brown University, Columbia University, Cornell University, Dartmouth College, Harvard University, University of Pennsylvania, Princeton University, and Yale University—however, the term is also used to connote academic excellence or social elitism. ↵
- “Directory of Representatives.” U.S. House of Representatives. https://www.house.gov/representatives. “Senators of the 116th Congress.” United States Senate. https://www.senate.gov/general/contact_information/senators_cfm.cfm. ↵
- Kyla Calvert Mason. 22 April 2014. “Percentage of Americans with College Degrees Rises, Paying for Degrees Tops Financial Challenges,” http://www.pbs.org/newshour/rundown/percentage-americans-college-degrees-rises-paying-degrees-tops-financial-challenges/. ↵
- Jennifer E. Manning. 24 November 2014. “Membership of the 113th Congress: A Profile.” Congressional Research Service, p. 3 (Table 2). ↵
- Drew Desilver. 18 December 2018. “A Record Number of Women Will be Serving in the New Congress.” FactTank. http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/12/18/record-number-women-in-congress/. ↵
- Karl Evers-Hillstrom, "Majority of lawmakers in 116th Congress are millionaires," 23 April 2020, https://www.opensecrets.org/news/2020/04/majority-of-lawmakers-millionaires/. ↵
- Lindsey Burke. 20 April 2009. “How Members of the 111th Congress Practice Private School Choice.” The Heritage Foundation. https://www.heritage.org/education/report/how-members-the-111th-congress-practice-private-school-choice. ↵
- “The Non-Governmental Order: Will NGOs Democratise, or Merely Disrupt, Global Governance?” The Economist, 9 December 1999. ↵
- Ronald J. Hrebenar. 1997. Interest Group Politics in America, 3rd ed. New York: Routledge, 14; Clive S. Thomas. 2004. Research Guide to U.S. and International Interest Groups. Westport, CT: Praeger, 106. ↵
- Dahl, Who Governs? 91–93. ↵
- McCullen v. Coakley, 573 U.S. 464 (2014); Melissa Jeltsen, “The Reality of Abortion Clinics without Buffer Zones,” The Huffington Post, 13 July 2014. ↵
- Gail Bambrick. 11 December 2012. “Fracking: Pro and Con,” https://now.tufts.edu/articles/fracking-pro-and-con. ↵
- “Gun Show Background Checks State Laws,” http://www.governing.com/gov-data/safety-justice/gun-show-firearms-bankground-checks-state-laws-map.html (February 18, 2016). ↵
- Russel Berman. 22 March 2018. "Congress's 'Baby Steps' on Guns." The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/politics/archive/2018/03/congress-guns-fix-nics-baby-steps/556250/ ↵
- "White House Weighs Executive Orders on Gun Control," New York Times, 24 March 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/2021/03/24/us/politics/white-house-gun-control-executive-orders.html. ↵
claims political power rests in the hands of a small, elite group of people
claims political power rests in the hands of groups of people

