Chapter 4: Civil Liberties
The Rights of Suspects
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the rights of those suspected or accused of criminal activity
- Explain how Supreme Court decisions transformed the rights of the accused
- Explain why the Eighth Amendment is controversial regarding capital punishment
In addition to protecting the personal freedoms of individuals, the Bill of Rights protects those suspected or accused of crimes from various forms of unfair or unjust treatment. The prominence of these protections in the Bill of Rights may seem surprising. Given the colonists’ experience of what they believed to be unjust rule by British authorities, however, and the use of the legal system to punish rebels and their sympathizers for political offenses, the impetus to ensure fair, just, and impartial treatment to everyone accused of a crime—no matter how unpopular—is perhaps more understandable. What is more, the revolutionaries, and the eventual framers of the Constitution, wanted to keep the best features of English law as well.
In addition to the protections outlined in the Fourth Amendment, which largely pertain to investigations conducted before someone has been charged with a crime, the next four amendments pertain to those suspected, accused, or convicted of crimes, as well as people engaged in other legal disputes. At every stage of the legal process, the Bill of Rights incorporates protections for these people.
*Watch this video to learn more about due process of law.
THE FIFTH AMENDMENT
Many of the provisions dealing with the rights of the accused are included in the Fifth Amendment; accordingly, it is one of the longest in the Bill of Rights. The Fifth Amendment states in full:
“No person shall be held to answer for a capital, or otherwise infamous crime, unless on a presentment or indictment of a Grand Jury, except in cases arising in the land or naval forces, or in the Militia, when in actual service in time of War or public danger; nor shall any person be subject for the same offence to be twice put in jeopardy of life or limb; nor shall be compelled in any criminal case to be a witness against himself, nor be deprived of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor shall private property be taken for public use, without just compensation.”
The first clause requires that serious crimes be prosecuted only after an indictment has been issued by a grand jury. However, several exceptions are permitted as a result of the evolving interpretation and understanding of this amendment by the courts, given the Constitution is a living document. First, the courts have generally found this requirement to apply only to felonies; less serious crimes can be tried without a grand jury proceeding. Second, this provision of the Bill of Rights does not apply to the states because it has not been incorporated; many states instead require a judge to hold a preliminary hearing to decide whether there is enough evidence to hold a full trial. Finally, members of the armed forces who are accused of crimes are not entitled to a grand jury proceeding.
The Fifth Amendment also protects individuals against double jeopardy, a process that subjects a suspect to prosecution twice for the same criminal act. No one who has been acquitted (found not guilty) of a crime can be prosecuted again for that crime. But the prohibition against double jeopardy has its own exceptions. The most notable is that it prohibits a second prosecution only at the same level of government (federal or state) as the first; the federal government can try you for violating federal law, even if a state or local court finds you not guilty of the same action. For example, in the early 1990s, several Los Angeles police officers accused of brutally beating motorist Rodney King during his arrest were acquitted of various charges in a state court, but some were later convicted in a federal court of violating King’s civil rights.
The double jeopardy rule does not prevent someone from recovering damages in a civil case—a legal dispute between individuals over a contract or compensation for an injury—that results from a criminal act, even if the person accused of that act is found not guilty. One famous case from the 1990s involved former football star and television personality O. J. Simpson. Simpson, although acquitted of the murders of his ex-wife Nicole Brown and her friend Ron Goldman in a criminal court, was later found to be responsible for their deaths in a subsequent civil case and as a result was forced to forfeit most of his wealth to pay damages to their families.
Perhaps the most famous provision of the Fifth Amendment is its protection against self-incrimination, or the right to remain silent. This provision is so well known that we have a phrase for it: “taking the Fifth.” People have the right not to give evidence in court or to law enforcement officers that might constitute an admission of guilt or responsibility for a crime. Moreover, in a criminal trial, if someone does not testify in their own defense, the prosecution cannot use that failure to testify as evidence of guilt or imply that an innocent person would testify. This provision became embedded in the public consciousness following the Supreme Court’s 1966 ruling in Miranda v. Arizona, whereby suspects were required to be informed of their most important rights, including the right against self-incrimination, before being interrogated in police custody.[1] However, contrary to some media depictions of the Miranda warning, law enforcement officials do not necessarily have to inform suspects of their rights before they are questioned in situations where they are free to leave.
Like the Fourteenth Amendment’s due process clause, the Fifth Amendment prohibits the federal government from depriving people of their “life, liberty, or property, without due process of law.” Recall that due process is a guarantee that people will be treated fairly and impartially by government officials when the government seeks to fine or imprison them or take their personal property away from them. The courts have interpreted this provision to mean that government officials must establish consistent, fair procedures to decide when people’s freedoms are limited. In other words, citizens cannot be detained, their freedom limited, or their property taken arbitrarily or on a whim by police or other government officials. As a result, an entire body of procedural safeguards comes into play for the legal prosecution of crimes. However, the Patriot Act, passed into law after the 9/11 terrorist attacks, somewhat altered this notion.
The final provision of the Fifth Amendment has little to do with crime at all. The takings clause says that “private property [cannot] be taken for public use, without just compensation.” This provision, along with the due process clause’s provisions limiting the taking of property, can be viewed as a protection of individuals’ economic liberty: their right to obtain, use, and trade tangible and intangible property for their own benefit. For example, you have the right to trade your knowledge, skills, and labor for money through work or the use of your property, or trade money or goods for other things of value, such as clothing, housing, education, or food.
A significant recent controversy over economic liberty has been sparked by cities’ and states’ use of the power of eminent domain to take property for redevelopment. Traditionally, the main use of eminent domain was to obtain property for transportation corridors like railroads, highways, canals and reservoirs, and pipelines, which require fairly straight routes to be efficient. Because any single property owner could effectively block a particular route or extract an unfair price for land if it was the last piece needed to assemble a route, there are reasonable arguments for using eminent domain as a last resort in these circumstances, particularly for projects that convey substantial benefits to the public at large.
However, increasingly eminent domain has been used to allow economic development, with beneficiaries ranging from politically connected big businesses such as car manufacturers building new factories to highly profitable sports teams seeking ever-more-luxurious stadiums (Figure 4.14). And, while we traditionally think of property owners as relatively well-off people who can fend for themselves in the political system and whose rights don’t necessarily need protecting, these cases frequently pit lower- and middle-class homeowners against multinational corporations or multimillionaires with the ear of city and state officials. In a notorious 2005 case, Kelo v. City of New London, the Supreme Court sided with municipal officials taking homes in a middle-class neighborhood to obtain land for a large pharmaceutical company’s corporate campus.[2] Ultimately, the campus was not built on the seized land and the case led to a public backlash against the use of eminent domain and legal changes in many states, making it harder for cities to take property from one private party and give it to another for economic redevelopment purposes. Eminent domain has once again become a salient issue in the context of the Trump administration’s attempt to use the doctrine to seize several parcels of private property for the proposed border wall.[3]

Some disputes over economic liberty have gone beyond the idea of eminent domain. In the past few years, companies seeking to offer profitable services online such as direct sales by electric car manufacturer Tesla Motors, on-demand ride-sharing services like Lyft and Uber, and short-term property rentals through companies like Airbnb have led to conflict with states and cities trying to regulate these businesses, and with incumbent service providers such as hotels and taxi cabs. In the absence of new public policies to clarify rights, the path forward is often determined through norms established by governments or by court cases.
Sometimes, however, the legislative process seeks to clarify or improve the interpretation and application of amendments. The Fifth Amendment Integrity Restoration Act is aimed at reducing the practice of civil forfeiture, in which governments and law enforcement entities seize property of people suspected of crimes, prior to conviction and sometimes without bringing formal charges. The government can take financial assets, jewelry, vehicles, art, and other items of value. The bipartisan bill backed by organizations ranging from the conservative-leaning Heritage Foundation to the ACLU, would reduce what its Senate sponsor, Rand Paul, refers to as “policing for profit.” Civil forfeiture was a mainstay of the war on drugs and contributed to the mass incarceration of people of color. It can be economically damaging even for those who are never charged or convicted, because in many cases seized property is not returned to its owner. Various court cases have ruled on aspects of the practice, but have not eliminated it derisively, leaving the opportunity for a new law to address it.
THE SIXTH AMENDMENT
Once someone has been charged with a crime and indicted, the next stage in a criminal case is typically the trial itself, unless a plea bargain is reached. The Sixth Amendment contains the provisions that govern criminal trials. I full, it states:
“In all criminal prosecutions, the accused shall enjoy the right to a speedy and public trial, by an impartial jury of the State and district wherein the crime shall have been committed, which district shall have been previously ascertained by law, and to be informed of the nature and cause of the accusation; to be confronted with the witnesses against him; to have compulsory process for obtaining witnesses in his favor, and to have the Assistance of Counsel for his defence [sic].”
The first of these guarantees is the right to have a speedy, public trial by an impartial jury. Although there is no absolute limit on the length of time that may pass between an indictment and a trial, the Supreme Court has said that excessively lengthy delays must be justified and balanced against the potential harm to the defendant.[4] In effect, the speedy trial requirement protects people from being detained indefinitely by the government. Yet the courts have ruled that there are exceptions to the public trial requirement; if a public trial would undermine the defendant’s right to a fair trial, it can be held behind closed doors, while prosecutors can request closed proceedings only in certain, narrow circumstances (generally, to protect witnesses from retaliation or to guard classified information). In general, a prosecution must also be made in the “state and district” where the crime was committed; however, people accused of crimes may ask for a change of venue for their trial if they believe pre-trial publicity or other factors make it difficult or impossible for them to receive a fair trial where the crime occurred.
LINK TO LEARNING
Although the Supreme Court’s proceedings are not televised and there is no video of the courtroom, audio recordings of the oral arguments and decisions announced in cases have been made since 1955. A complete collection of these recordings can be found at the Oyez Project website along with full information about each case.
Most people accused of crimes decline their right to a jury trial. This choice is typically the result of a plea bargain, an agreement between the defendant and the prosecutor in which the defendant pleads guilty to the charge(s) in question, or perhaps to less serious charges, in exchange for more lenient punishment than they might receive if convicted after a full trial. There are a number of reasons why this might happen. The evidence against the accused may be so overwhelming that conviction is a near-certainty, so the accused might decide that avoiding the more serious penalty (perhaps even the death penalty) is better than taking the small chance of being acquitted after a trial. Someone accused of being part of a larger crime or criminal organization might agree to testify against others in exchange for lighter punishment. At the same time, prosecutors might want to ensure a win in a case that might not hold up in court by securing convictions for offenses they know they can prove, while avoiding a lengthy trial on other charges they might lose.
The requirement that a jury be impartial is a critical requirement of the Sixth Amendment. Both the prosecution and the defense are permitted to reject potential jurors who they believe are unable to fairly decide the case without prejudice. However, the courts have also said that the composition of the jury as a whole may in itself be prejudicial, so potential jurors may not be rejected simply because of their race or sex, for example.[5]
The Sixth Amendment guarantees the right of those accused of crimes to present witnesses in their own defense (if necessary, compelling them to testify) and to confront and cross-examine witnesses presented by the prosecution. In general, the only testimony acceptable in a criminal trial must be given in a courtroom and be subject to cross-examination; hearsay, or testimony by one person about what another person has said, is generally inadmissible, although hearsay may be presented as evidence when it is an admission of guilt by the defendant or a “dying declaration” by a person who has passed away. Although both sides in a trial have the opportunity to examine and cross-examine witnesses, the judge may exclude testimony deemed irrelevant or prejudicial.
Finally, the Sixth Amendment guarantees the right of those accused of crimes to have the assistance of an attorney in their defense. Historically, many states did not provide attorneys to those accused of most crimes who could not afford one themselves, and even when an attorney was provided, their assistance was often inadequate, at best. This situation changed as a result of the Supreme Court’s decision in Gideon v. Wainwright (1963).[6] Clarence Gideon, a poor drifter, was accused of breaking into and stealing money and other items from a pool hall in Panama City, Florida. Denied a lawyer, Gideon was tried and convicted and sentenced to a five-year prison term. While in prison and still without assistance of a lawyer, he drafted a handwritten appeal and sent it to the Supreme Court, which agreed to hear his case (Figure 4.15). The justices unanimously ruled that Gideon, and anyone else accused of a serious crime, was entitled to the assistance of a lawyer, even if they could not afford one, as part of the general due process right to a fair trial.

The Supreme Court later extended the Gideon v. Wainwright ruling to apply to any case in which an accused person faced the possibility of “loss of liberty,” even for one day. The courts have also overturned convictions in which people had incompetent or ineffective lawyers through no fault of their own. The Gideon ruling has led to an increased need for professional public defenders, lawyers who are paid by the government to represent those who cannot afford an attorney themselves, although some states instead require practicing lawyers to represent poor defendants on a pro bono basis (essentially, donating their time and energy to the case).
LINK TO LEARNING
The National Association for Public Defense represents public defenders, lobbying for better funding for public defense and improvements in the justice system in general.
INSIDER PERSPECTIVE
Criminal Justice: Theory Meets Practice
Typically, a person charged with a serious crime will have a brief hearing before a judge to be informed of the charges against the person, to be made aware of the right to counsel, and to enter a plea. Other hearings may be held to decide on the admissibility of evidence seized or otherwise obtained by prosecutors.
If the two sides cannot agree on a plea bargain during this period, the next stage is the selection of a jury. A pool of potential jurors is summoned to the court and screened for impartiality, with the goal of seating twelve (in most states) and one or two alternates. All hear the evidence in the trial and unless an alternate must serve, the original twelve decide whether the evidence overwhelmingly points toward guilt, or innocence beyond a reasonable doubt.
In the trial itself, the lawyers for the prosecution and defense make opening arguments, followed by testimony by witnesses for the prosecution (and any cross-examination), and then testimony by witnesses for the defense, including the defendant if the defendant chooses. Additional prosecution witnesses may be called to rebut testimony by the defense. Finally, both sides make closing arguments. The judge then issues instructions to the jury, including an admonition not to discuss the case with anyone outside the jury room. The jury members leave the courtroom to enter the jury room and begin their deliberations (Figure 4.16).

The jurors pick a foreman or forewoman to coordinate their deliberations. They may ask to review evidence or to hear transcripts of testimony. They deliberate in secret and their decision must be unanimous. If they are unable to agree on a verdict after extensive deliberation, a mistrial may be declared, which in effect requires the prosecution to try the case all over again.
A defendant found not guilty of all charges will be immediately released unless other charges are pending (e.g., the defendant is wanted for a crime in another jurisdiction). If the defendant is found guilty of one or more offenses, the judge will choose an appropriate sentence based on the law and the circumstances. In the federal system, this sentence will typically be based on guidelines that assign point values to various offenses and facts in the case. If the prosecution is pursuing the death penalty, the jury will decide whether the defendant should be subject to capital punishment or life imprisonment.
The reality of court procedure is much less dramatic and exciting than what is typically portrayed in television shows and movies. Nonetheless, most Americans will participate in the legal system at least once in their lives as a witness, juror, or defendant.
Have you or any member of your family served on a jury? If so, was the experience a positive one? Did the trial proceed as expected? If you haven’t served on a jury, is it something you look forward to? Why or why not?
THE SEVENTH AMENDMENT
The Seventh Amendment deals with the rights of those engaged in civil disputes—disagreements between individuals or businesses in which people are typically seeking compensation for some harm caused. For example, in an automobile accident, the person responsible is compelled to compensate any others (either directly or through their insurance company). Much of the work of the legal system consists of efforts to resolve civil disputes. The Seventh Amendment, in full, reads:
“In Suits at common law, where the value in controversy shall exceed twenty dollars, the right of trial by jury shall be preserved, and no fact tried by a jury, shall be otherwise re-examined in any Court of the United States, than according to the rules of the common law.”
Because of this provision, all trials in civil cases must take place before a jury unless both sides waive their right to a jury trial. However, this right is not always incorporated. In many states, civil disputes—particularly those involving small sums of money, which may be heard by a dedicated small claims court—need not be tried in front of a jury and may instead be decided by a judge working alone.
The Seventh Amendment limits the ability of judges to reconsider questions of fact, rather than of law, that were originally decided by a jury. For example, if a jury decides a person was responsible for an action and the case is appealed, the appeals judge cannot decide someone else was responsible. This preserves the traditional common-law distinction that judges are responsible for deciding questions of law while jurors are responsible for determining the facts of a particular case.
THE EIGHTH AMENDMENT
The Eighth Amendment says, in full:
“Excessive bail shall not be required, nor excessive fines imposed, nor cruel and unusual punishments inflicted.”
Bail is a payment of money that allows a person accused of a crime to be freed pending trial. If you “make bail” in a case and do not show up for your trial, you will forfeit the money you paid. Since many people cannot afford to pay bail directly, they may instead get a bail bond, which allows them to pay a fraction of the money (typically 10 percent) to a person who sells bonds and who pays the full bail amount. (In most states, the bond seller makes money because the defendant does not get back the money for the bond, and most people show up for their trials.) However, people believed likely to flee or who represent a risk to the community while free may be denied bail and held in jail until their trial takes place.
It is rare for bail to be successfully challenged for being excessive. The Supreme Court has defined an excessive fine as one “so grossly excessive as to amount to deprivation of property without due process of law” or “grossly disproportional to the gravity of a defendant’s offense.”[7] Historically, the courts have rarely struck down fines as excessive, though California and other states have recently passed legislation seeking to reform the more discriminatory aspects of the bail system.
The most controversial provision of the Eighth Amendment is the ban on “cruel and unusual punishments.” Various torturous forms of execution common in the past—drawing and quartering, burning people alive, and the electric chair—are prohibited by this provision.[8] Recent controversies over lethal injections and firing squads demonstrate that the topic of whether and how to execute is still very much alive. The Dutch producer of one of the chemicals in the most common lethal injection cocktail recently refused to export it to the United States when it was shown to protract the dying process for some inmates, maintaining consciousness, prolonging suffering, and paralyzing response. In a 2021 case, one death row prisoner lost an appeal to request death by firing squad in lieu of lethal injection. While the Supreme Court has never established a definitive test for what constitutes a cruel and unusual punishment, it has generally allowed most penalties short of death for adults, even when the punishment appears disproportionate or excessive to outside observers.[9]
In recent years the Supreme Court has issued a series of rulings substantially narrowing the application of the death penalty. As a result, defendants who have intellectual disabilities may not be executed.[10] Defendants who were under eighteen when they committed an offense that would otherwise be subject to the death penalty may not be executed.[11] The court has generally rejected the application of the death penalty to crimes that did not result in the death of another human being, most notably in the case of rape.[12] And, while permitting the death penalty to be applied to murder in some cases, the Supreme Court has generally struck down laws that require the application of the death penalty in certain circumstances. Still, the United States is among ten countries with the most executions worldwide, with the Trump Justice Department pushing through a flurry of thirteen executions in the last four months of his administration, breaking with the 130-year-old precedent of pausing executions amid a presidential transition (Figure 4.17).
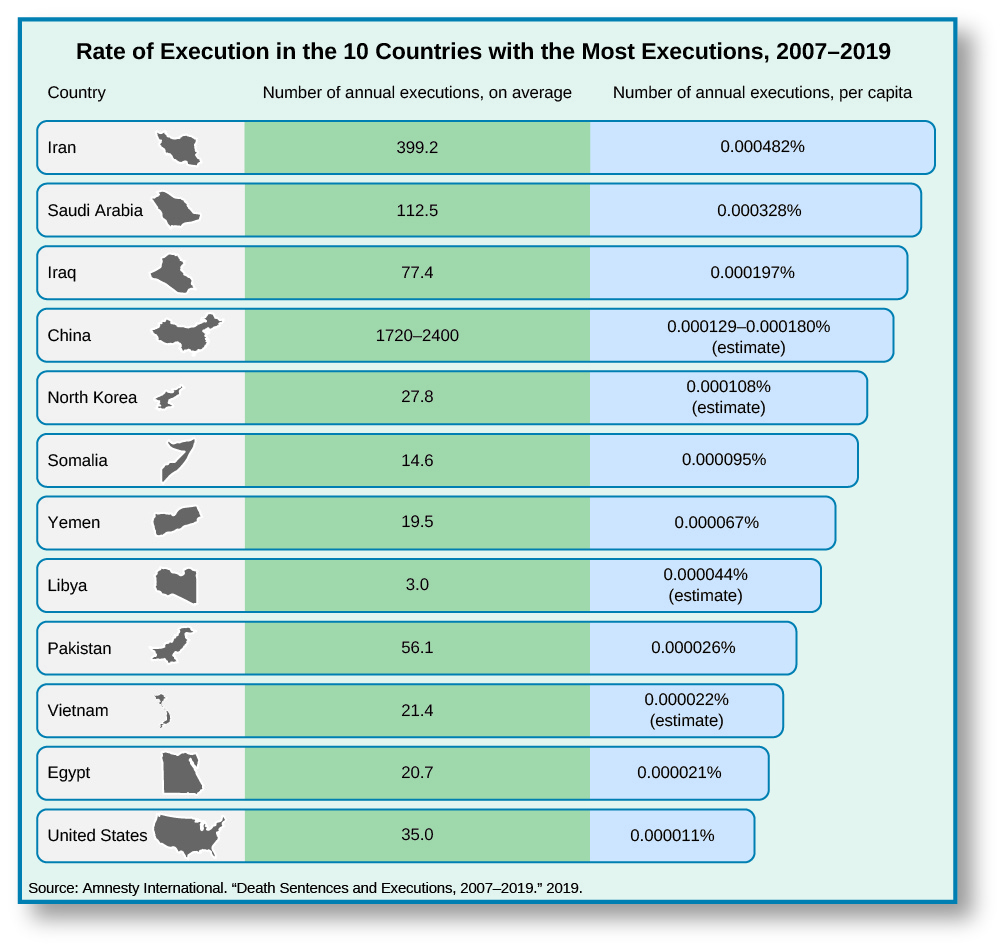
At the same time, however, it appears that the public mood may have shifted somewhat against the death penalty, perhaps due in part to an overall decline in violent crime. The reexamination of past cases through DNA evidence has revealed dozens in which people were wrongfully executed.[13] For example, Claude Jones was executed for murder based on 1990-era DNA testing of a single hair that was determined at that time to be his but that with better DNA testing technology was later found to be that of the victim.[14] Perhaps as a result of this and other cases, seven additional states have abolished capital punishment since 2007. As of 2015, nineteen states and the District of Columbia no longer apply the death penalty in new cases, and several other states do not carry out executions despite sentencing people to death.[15] It remains to be seen whether this gradual trend toward the elimination of the death penalty by the states will continue, or whether the Supreme Court will eventually decide to follow former Justice Harry Blackmun’s decision to “no longer… tinker with the machinery of death” and abolish it completely.
CHAPTER REVIEW
See the Chapter 4.3 Review for a summary of this section, the key vocabulary, and some review questions to check your knowledge.
- Miranda v. Arizona, 384 U.S. 436 (1966). ↵
- Kelo et al. v. City of New London et al., 545 U.S. 469 (2005). ↵
- John C. Moritz. 27 November 2018. "Catholic Diocese Fights to Keep Historic Site from Being Used in Trump's Border Wall." Corpus Christi Caller Times. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/politics/2018/11/27/texas-la-lomita-mission-center-border-wall-eminent-domain-fight/2132582002/. ↵
- See, for example, Barker v. Wingo, 407 U.S. 514 (1972). ↵
- See, for example, Batson v. Kentucky, 476 U.S. 79 (1986); J. E. B. v. Alabama ex rel. T. B., 511 U.S. 127 (1994). ↵
- Gideon v. Wainwright, 372 U.S. 335 (1963). ↵
- Waters-Pierce Oil Co. v. Texas, 212 U.S. 86 (1909); United States v. Bajakajian, 524 U.S. 321 (1998). ↵
- See, for example, the discussion in Wilkerson v. Utah, 99 U.S. 130 (1879). ↵
- Perhaps the most notorious example, Harmelin v. Michigan, 501 U.S. 957 (1991), upheld a life sentence in a case where the defendant was convicted of possessing just over one pound of cocaine (and no other crime). ↵
- Atkins v. Virginia, 536 U.S. 304 (2002). ↵
- Roper v. Simmons, 543 U.S. 551 (2005). ↵
- Kennedy v. Louisiana, 554 U.S. 407 (2008). ↵
- Elizabeth Lopatto, “How Many Innocent People Are Sentenced To Death?,” Forbes, 29 April 2014. http://www.forbes.com/sites/elizabethlopatto/2014/04/29/how-many-innocent-people-are-sentenced-to-death/#6e9ae5175cc1 (March 1, 2016). ↵
- Dave Mann, “DNA Tests Undermine Evidence in Texas Execution: New Results Show Claude Jones was Put to Death on Flawed Evidence,” Texas Observer, 11 November 2010. http://www.texasobserver.org/texas-observer-exclusive-dna-tests-undermine-evidence-in-texas-execution/ (March 4, 2016). ↵
- See, for example, “States With and Without the Death Penalty,” Death Penalty Information Center, http://www.deathpenaltyinfo.org/states-and-without-death-penalty (March 4, 2016). ↵
a prosecution pursued twice at the same level of government for the same criminal action
an action or statement that admits guilt or responsibility for a crime
a statement by law enforcement officers informing a person arrested, or subject to interrogation, of that person's rights
the right of individuals to obtain, use, and trade things of value for their own benefit
the power of government to take or use property for a public purpose after compensating its owner; also known as the takings clause of the Fifth Amendment
an agreement between the defendant and the prosecutor in which the defendant pleads guilty to the charge(s) in question or perhaps to less serious charges, in exchange for more lenient punishment than if convicted after a full trial

