Chapter 3: American Federalism
The Evolution of American Federalism
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe how federalism has evolved in the United States
- Compare different conceptions of federalism
The Constitution sketches a federal framework that aims to balance the forces of decentralized and centralized governance in general terms; it does not flesh out standard operating procedures that say precisely how the states and federal governments are to handle all policy contingencies imaginable. Therefore, officials at the state and national levels have had some room to maneuver as they operate within the Constitution’s federal design. This has led to changes in the configuration of federalism over time, changes corresponding to different historical phases that capture distinct balances between state and federal authority.
THE STRUGGLE BETWEEN NATIONAL POWER AND STATE POWER
As George Washington’s secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795, Alexander Hamilton championed legislative efforts to create a publicly chartered bank. For Hamilton, the establishment of the Bank of the United States was fully within Congress’s authority, and he hoped the bank would foster economic development, print and circulate paper money, and provide loans to the government. Although Thomas Jefferson, Washington’s secretary of state, staunchly opposed Hamilton’s plan on the constitutional grounds that the national government had no authority to create such an instrument, Hamilton managed to convince the reluctant president to sign the legislation.[1]
When the bank’s charter expired in 1811, Jeffersonian Democratic-Republicans prevailed in blocking its renewal. However, the fiscal hardships that plagued the government during the War of 1812, coupled with the fragility of the country’s financial system, convinced Congress and then-president James Madison to create the Second Bank of the United States in 1816. Many states rejected the Second Bank, arguing that the national government was infringing upon the states’ constitutional jurisdiction.
A political showdown between Maryland and the national government emerged when James McCulloch, an agent for the Baltimore branch of the Second Bank, refused to pay a tax that Maryland had imposed on all out-of-state chartered banks. The standoff raised two constitutional questions: Did Congress have the authority to charter a national bank? Were states allowed to tax federal property? In McCulloch v. Maryland, Chief Justice John Marshall (Figure 3.8) argued that Congress could create a national bank even though the Constitution did not expressly authorize it.[2] Under the necessary and proper clause of Article I, Section 8, the Supreme Court asserted that Congress could establish “all means which are appropriate” to fulfill “the legitimate ends” of the Constitution. In other words, the bank was an appropriate instrument that enabled the national government to carry out several of its enumerated powers, such as regulating interstate commerce, collecting taxes, and borrowing money.

This ruling established the doctrine of implied powers, granting Congress a vast source of discretionary power to achieve its constitutional responsibilities. The Supreme Court also sided with the federal government on the issue of whether states could tax federal property. Under the supremacy clause of Article VI, legitimate national laws trump conflicting state laws. As the court observed, “the government of the Union, though limited in its powers, is supreme within its sphere of action and its laws, when made in pursuance of the constitution, form the supreme law of the land.” Maryland’s action violated national supremacy because “the power to tax is the power to destroy.” This second ruling established the principle of national supremacy, which prohibits states from meddling in the lawful activities of the national government.
Defining the scope of national power was the subject of another landmark Supreme Court decision in 1824. In Gibbons v. Ogden, the court had to interpret the commerce clause of Article I, Section 8; specifically, it had to determine whether the federal government had the sole authority to regulate the licensing of steamboats operating between New York and New Jersey.[3] Aaron Ogden, who had obtained an exclusive license from New York State to operate steamboat ferries between New York City and New Jersey, sued Thomas Gibbons, who was operating ferries along the same route under a coasting license issued by the federal government. Gibbons lost in New York state courts and appealed. Chief Justice Marshall delivered a two-part ruling in favor of Gibbons that strengthened the power of the national government. First, interstate commerce was interpreted broadly to mean “commercial intercourse” among states, thus allowing Congress to regulate navigation. Second, because the federal Licensing Act of 1793, which regulated coastal commerce, was a constitutional exercise of Congress’s authority under the commerce clause, federal law trumped the New York State license-monopoly law that had granted Ogden an exclusive steamboat operating license. As Marshall pointed out, “the acts of New York must yield to the law of Congress.”[4]
Various states railed against the nationalization of power that had been going on since the late 1700s. When President John Adams signed the Sedition Act in 1798, which made it a crime to speak openly against the government, the Kentucky and Virginia legislatures passed resolutions declaring the act null on the grounds that they retained the discretion to follow national laws. In effect, these resolutions articulated the legal reasoning underpinning the doctrine of nullification—that states had the right to reject national laws they deemed unconstitutional.[5]
A nullification crisis emerged in the 1830s over President Andrew Jackson’s tariff acts of 1828 and 1832. Led by John Calhoun, President Jackson’s vice president, nullifiers argued that high tariffs on imported goods benefited northern manufacturing interests while disadvantaging economies in the South. South Carolina passed an Ordinance of Nullification declaring both tariff acts null and void and threatened to leave the Union. The federal government responded by enacting the Force Bill in 1833, authorizing President Jackson to use military force against states that challenged federal tariff laws. The prospect of military action coupled with the passage of the Compromise Tariff Act of 1833 (which lowered tariffs over time) led South Carolina to back off, ending the nullification crisis.
The ultimate showdown between national and state authority came during the Civil War. Prior to the conflict, in Dred Scott v. Sandford, the Supreme Court ruled that the national government lacked the authority to ban slavery in the territories.[6] But the election of President Abraham Lincoln in 1860 led eleven southern states to secede from the United States because they believed the new president would challenge the institution of slavery. What was initially a conflict to preserve the Union became a conflict to end slavery when Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863, freeing all enslaved people in the rebellious states. The defeat of the South had a huge impact on the balance of power between the states and the national government in two important ways. First, the Union victory put an end to the right of states to secede and to challenge legitimate national laws. Second, Congress imposed several conditions for readmitting former Confederate states into the Union; among them was ratification of the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments. In sum, after the Civil War the power balance shifted toward the national government, a movement that had begun several decades before with McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) and Gibbons v. Odgen (1824).
The period between 1819 and the 1860s demonstrated that the national government sought to establish its role within the newly created federal design, which in turn often provoked the states to resist as they sought to protect their interests. With the exception of the Civil War, the Supreme Court settled the power struggles between the states and national government. From a historical perspective, the national supremacy principle introduced during this period did not so much narrow the states’ scope of constitutional authority as restrict their encroachment on national powers.[7]
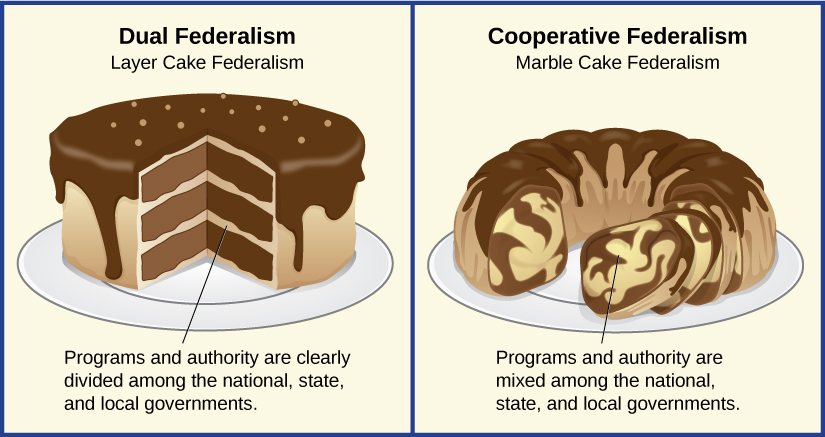
DUAL FEDERALISM
The late 1870s ushered in a new phase in the evolution of U.S. federalism. Under dual federalism, the states and national government exercise exclusive authority in distinctly delineated spheres of jurisdiction. Like the layers of a cake, the levels of government do not blend with one another but rather are clearly defined. Two factors contributed to the emergence of this conception of federalism. First, several Supreme Court rulings blocked attempts by both state and federal governments to step outside their jurisdictional boundaries. Second, the prevailing economic philosophy at the time loathed government interference in the process of industrial development.
Industrialization changed the socioeconomic landscape of the United States. One of its adverse effects was the concentration of market power. Because there was no national regulatory supervision to ensure fairness in market practices, collusive behavior among powerful firms emerged in several industries.[8] To curtail widespread anticompetitive practices in the railroad industry, Congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act in 1887, which created the Interstate Commerce Commission. Three years later, national regulatory capacity was broadened by the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, which made it illegal to monopolize or attempt to monopolize and conspire in restraining commerce (Figure 3.9). In the early stages of industrial capitalism, federal regulations were focused for the most part on promoting market competition rather than on addressing the social dislocations resulting from market operations, something the government began to tackle in the 1930s.[9]

The new federal regulatory regime was dealt a legal blow early in its existence. In 1895, in United States v. E. C. Knight, the Supreme Court ruled that the national government lacked the authority to regulate manufacturing.[10] The case came about when the government, using its regulatory power under the Sherman Act, attempted to override American Sugar’s purchase of four sugar refineries, which would give the company a commanding share of the industry. Distinguishing between commerce among states and the production of goods, the court argued that the national government’s regulatory authority applied only to commercial activities. If manufacturing activities fell within the purview of the commerce clause of the Constitution, then “comparatively little of business operations would be left for state control,” the court argued.
In the late 1800s, some states attempted to regulate working conditions. For example, New York State passed the Bakeshop Act in 1897, which prohibited bakery employees from working more than sixty hours in a week. In Lochner v. New York, the Supreme Court ruled this state regulation that capped work hours unconstitutional, on the grounds that it violated the due process clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.[11] In other words, the right to sell and buy labor is a “liberty of the individual” safeguarded by the Constitution, the court asserted. The federal government also took up the issue of working conditions, but that case resulted in the same outcome as in the Lochner case.[12]
COOPERATIVE FEDERALISM
The Great Depression of the 1930s brought economic hardships the nation had never witnessed before (Figure 3.10). Between 1929 and 1933, the national unemployment rate reached 25 percent, industrial output dropped by half, stock market assets lost more than half their value, thousands of banks went out of business, and the gross domestic product shrunk by one-quarter.[13] Given the magnitude of the economic depression, there was pressure on the national government to coordinate a robust national response along with the states.

Cooperative federalism was born of necessity and lasted well into the twentieth century as the national and state governments each found it beneficial. Under this model, both levels of government coordinated their actions to solve national problems, such as the Great Depression and the civil rights struggle of the following decades. In contrast to dual federalism, it erodes the jurisdictional boundaries between the states and national government, leading to a blending of layers as in a marble cake. The era of cooperative federalism contributed to the gradual incursion of national authority into the jurisdictional domain of the states, as well as the expansion of the national government’s power in concurrent policy areas.[14]
The New Deal programs President Franklin D. Roosevelt proposed as a means to tackle the Great Depression ran afoul of the dual-federalism mindset of the justices on the Supreme Court in the 1930s. The court struck down key pillars of the New Deal—the National Industrial Recovery Act and the Agricultural Adjustment Act, for example—on the grounds that the federal government was operating in matters that were within the purview of the states. The court’s obstructionist position infuriated Roosevelt, leading him in 1937 to propose a court-packing plan that would add one new justice for each one over the age of seventy, thus allowing the president to make a maximum of six new appointments. Before Congress took action on the proposal, the Supreme Court began leaning in support of the New Deal as Chief Justice Charles Evans Hughes and Justice Owen Roberts changed their view on federalism.[15]
In National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) v. Jones and Laughlin Steel,[16] for instance, the Supreme Court ruled the National Labor Relations Act of 1935 constitutional, asserting that Congress can use its authority under the commerce clause to regulate both manufacturing activities and labor-management relations. The New Deal changed the relationship Americans had with the national government. Before the Great Depression, the government offered little in terms of financial aid, social benefits, and economic rights. After the New Deal, it provided old-age pensions (Social Security), unemployment insurance, agricultural subsidies, protections for organizing in the workplace, and a variety of other public services created during Roosevelt’s administration.
In the 1960s, President Lyndon Johnson’s administration expanded the national government’s role in society even more. Medicaid (which provides medical assistance to the indigent), Medicare (which provides health insurance to the elderly and some people with disabilities), and school nutrition programs were created. The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (1965), the Higher Education Act (1965), and the Head Start preschool program (1965) were established to expand educational opportunities and equality (Figure 3.12). The Clean Air Act (1965), the Highway Safety Act (1966), and the Fair Packaging and Labeling Act (1966) promoted environmental and consumer protection. Finally, laws were passed to promote urban renewal, public housing development, and affordable housing. In addition to these Great Society programs, the Civil Rights Act (1964) and the Voting Rights Act (1965) gave the federal government effective tools to promote civil rights equality across the country.

While the era of cooperative federalism witnessed a broadening of federal powers in concurrent and state policy domains, it is also the era of a deepening coordination between the states and the federal government in Washington. Nowhere is this clearer than with respect to the social welfare and social insurance programs created during the New Deal and Great Society eras, most of which are administered by both state and federal authorities and are jointly funded. The Social Security Act of 1935, which created federal subsidies for state-administered programs for the elderly; people with disabilities; dependent mothers; and children, gave state and local officials wide discretion over eligibility and benefit levels. The unemployment insurance program, also created by the Social Security Act, requires states to provide jobless benefits, but it allows them significant latitude to decide the level of tax to impose on businesses in order to fund the program as well as the duration and replacement rate of unemployment benefits. A similar multilevel division of labor governs Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance.[17]
Thus, the era of cooperative federalism left two lasting attributes on federalism in the United States. First, a nationalization of politics emerged as a result of federal legislative activism aimed at addressing national problems such as marketplace inefficiencies, social and political inequality, and poverty. The nationalization process expanded the size of the federal administrative apparatus and increased the flow of federal grants to state and local authorities, which have helped offset the financial costs of maintaining a host of New Deal- and Great Society–era programs. The second lasting attribute is the flexibility that states and local authorities were given in the implementation of federal social welfare programs. One consequence of administrative flexibility, however, is that it has led to cross-state differences in the levels of benefits and coverage.[18]
NEW FEDERALISM
During the administrations of Presidents Richard Nixon (1969–1974) and Ronald Reagan (1981–1989), attempts were made to reverse the process of nationalization—that is, to restore states’ prominence in policy areas into which the federal government had moved in the past. New federalism is premised on the idea that the decentralization of policies enhances administrative efficiency, reduces overall public spending, and improves policy outcomes. During Nixon’s administration, general revenue sharing programs were created that distributed funds to the state and local governments with minimal restrictions on how the money was spent. The election of Ronald Reagan heralded the advent of a “devolution revolution” in U.S. federalism, in which the president pledged to return authority to the states according to the Constitution. In the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1981, congressional leaders together with President Reagan consolidated numerous federal grant programs related to social welfare and reformulated them in order to give state and local administrators greater discretion in using federal funds.[19]
However, Reagan’s track record in promoting new federalism was inconsistent. This was partly due to the fact that the president’s devolution agenda met some opposition from Democrats in Congress, moderate Republicans, and interest groups, preventing him from making further advances on that front. For example, his efforts to completely devolve Aid to Families With Dependent Children (a New Deal-era program) and food stamps (a Great Society-era program) to the states were rejected by members of Congress, who feared states would underfund both programs, and by members of the National Governors’ Association, who believed the proposal would be too costly for states. Reagan terminated general revenue sharing in 1986.[20]
Several Supreme Court rulings also promoted new federalism by hemming in the scope of the national government’s power, especially under the commerce clause. For example, in United States v. Lopez, the court struck down the Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990, which banned gun possession in school zones.[21] It argued that the regulation in question did not “substantively affect interstate commerce.” The ruling ended a nearly sixty-year period in which the court had used a broad interpretation of the commerce clause that by the 1960s allowed it to regulate numerous local commercial activities.[22]
However, many would say that the years since the 9/11 attacks have swung the pendulum back in the direction of central federal power. The creation of the Department of Homeland Security federalized disaster response power in Washington, and the Transportation Security Administration was created to federalize airport security. Broad new federal policies and mandates have also been carried out in the form of the Faith-Based Initiative and No Child Left Behind (during the George W. Bush administration) and the Affordable Care Act (during Barack Obama’s administration).
FINDING A MIDDLE GROUND
Cooperative Federalism versus New Federalism
The challenges of the 1930s led many to question the merits of dual federalism, where the states and the national governments exercised exclusive authority in distinctly delineated spheres of jurisdiction. The result was the birth of cooperative federalism. In this view of federalism, the jurisdictional boundaries between the national and state governments were eroded to allow for greater cooperation between both governments. While this expansion of national government power was crucial in tackling the problems of the Great Depression, environmental degradation, and civil rights abuses, many resented the federal incursions into what had earlier been state matters. These concerns led to the emergence of new federalism in the 1970s and ’80s. New federalism was premised on the idea that the decentralization of policies enhanced administrative efficiency and improved outcomes. Rather than simply a return to the old dual federalism model, new federalism continued much of the federal spending but rolled back many of the restrictions on what states could do with their federal funds.
Cooperative federalism has several merits:
- Because state and local governments have varying fiscal capacities, the national government’s involvement in state activities such as education, health, and social welfare is necessary to ensure some degree of uniformity in the provision of public services to citizens in richer and poorer states.
- The problem of collective action, which dissuades state and local authorities from raising regulatory standards for fear they will be disadvantaged as others lower theirs, is resolved by requiring state and local authorities to meet minimum federal standards (e.g., minimum wage and air quality).
- Federal assistance is necessary to ensure state and local programs that generate positive externalities are maintained. For example, one state’s environmental regulations impose higher fuel prices on its residents, but the externality of the cleaner air they produce benefits neighboring states. Without the federal government’s support, this state and others like it would underfund such programs.
New federalism has advantages as well:
- Because of differences among states, one-size-fits-all features of federal laws are suboptimal. Decentralization accommodates the diversity that exists across states.
- By virtue of being closer to citizens, state and local authorities are better than federal agencies at discerning the public’s needs.
- Decentralized federalism fosters a marketplace of innovative policy ideas as states compete against each other to minimize administrative costs and maximize policy output.
Which model of federalism do you think works best for the United States? Why?
LINK TO LEARNING
The leading international journal devoted to the practical and theoretical study of federalism is called Publius: The Journal of Federalism. Find out where its name comes from.
CHAPTER REVIEW
See the Chapter 3.2 Review for a summary of this section, the key vocabulary, and some review questions to check your knowledge.
- The Lehrman Institute. “The Founding Trio: Washington, Hamilton and Jefferson.” http://lehrmaninstitute.org/history/FoundingTrio.asp ↵
- McCulloch v. Maryland, 17 U.S. 316 (1819). ↵
- Gibbons v. Ogden, 22 U.S. 1 (1824). ↵
- Gibbons v. Ogden, 22 U.S. 1 (1824). ↵
- W. Kirk Wood. 2008. Nullification, A Constitutional History, 1776–1833. Lanham, MD: University Press of America. ↵
- Dred Scott v. Sandford, 60 U.S. 393 (1857). ↵
- Joseph R. Marbach, Troy E. Smith, and Ellis Katz. 2005. Federalism in America: An Encyclopedia. Westport, CT: Greenwood Publishing. ↵
- Marc Allen Eisner. 2014. The American Political Economy: Institutional Evolution of Market and State. New York: Routledge. ↵
- Eisner, The American Political Economy; Stephen Skowronek. 1982. Building a New American State: The Expansion of National Administrative Capacities, 1877–1920. Cambridge, MA: Cambridge University Press. ↵
- United States v. E. C. Knight, 1sometimes referred to as the Sugar Trust case, 56 U.S. 1 (1895). ↵
- Lochner v. New York, 198 U.S. 45 (1905). ↵
- Hammer v. Dagenhart, 247 U.S. 251 (1918). ↵
- Nicholas Crafts and Peter Fearon. 2010. “Lessons from the 1930s Great Depression,” Oxford Review of Economic Policy 26: 286–287; Gene Smiley. “The Concise Encyclopedia of Economics: Great Depression.” http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/GreatDepression.html ↵
- Marbach et al, Federalism in America: An Encyclopedia. ↵
- Jeff Shesol. 2010. Supreme Power: Franklin Roosevelt vs. The Supreme Court. New York: W. W. Norton. ↵
- National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) v. Jones & Laughlin Steel, 301 U.S. 1 (1937). ↵
- Lawrence R. Jacobs and Theda Skocpol. 2014. “Progressive Federalism and the Contested Implemented of Obama’s Health Reform,” In The Politics of Major Policy Reform in Postwar America, eds. Jeffrey A. Jenkins and Sidney M. Milkis. New York: Cambridge University Press. ↵
- R. Kent Weaver. 2000. Ending Welfare as We Know It. Washington, DC: The Brookings Institution. ↵
- Allen Schick. 2007. The Federal Budget, 3rd ed. Washington, DC: The Brookings Institution. ↵
- Dilger, “Federal Grants to State and Local Governments,” 30–31. ↵
- United States v. Lopez, 514 U.S. 549 (1995). ↵
- See Printz v. United States, 521 U.S. 898 (1997). ↵
a doctrine promoted by John Calhoun of South Carolina in the 1830s, asserting that if a state deems a federal law unconstitutional, it can nullify it within its borders
a style of federalism in which the states and national government exercise exclusive authority in distinctly delineated spheres of jurisdiction, creating a layer-cake view of federalism
a style of federalism in which both levels of government coordinate their actions to solve national problems, leading to the blending of layers as in a marble cake
a style of federalism premised on the idea that the decentralization of policies enhances administrative efficiency, reduces overall public spending, and improves outcomes
a type of federal grant that places minimal restrictions on how state and local governments spend the money

